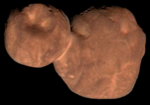
Radar images of 2016 AZ8 and its satellite by the Arecibo Observatory in January 2019 | |
| Discovery[1] | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | WISE |
| Discovery site | Earth orbit |
| Discovery date | 3 January 2016 |
| Designations | |
| 2016 AZ8 | |
| NEO · Apollo[1][2] PHA[1][2] | |
| Orbital characteristics[2] | |
| Epoch 27 April 2019 (JD 2458600.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 0 | |
| Observation arc | 3.69 yr (1,347 d) |
| Aphelion | 1.7895 AU |
| Perihelion | 0.8516 AU |
| 1.3205 AU | |
| Eccentricity | 0.3551 |
| 1.52 yr (554 d) | |
| 99.623° | |
| 0° 38m 58.2s / day | |
| Inclination | 5.5862° |
| 90.016° | |
| 318.51° | |
| Known satellites | 1[3] |
| Earth MOID | 0.0295 AU (11.49 LD) |
| Physical characteristics | |
Mean diameter | 215±52 m[2] |
| 21.0[2] | |
2016 AZ8 is a sub-kilometer asteroid and near-Earth object of the Apollo group, at least 400 meters (1,300 feet) in diameter.[1][3] It was first observed on 3 January 2016, by the WISE telescope with precovery images found back in 2012.
The potentially hazardous asteroid is a binary system with a minor-planet moon in its orbit. The discovery was made by astronomers at Arecibo Observatory on 4 January 2019, while 2016 AZ8 was passing within 4,460,000 kilometers (0.0298 AU) of the Earth.[3] The binary has a secondary-to-primary diameter ratio of at least 0.3.[3]
Orbit and classification
2016 AZ8 orbits the Sun at a distance of 0.85–1.8 AU once every 18 months (554 days; semi-major axis of 1.32 AU). Its orbit has an eccentricity of 0.36 and an inclination of 6° with respect to the ecliptic.[2] The body's observation arc begins with a precovery taken at the Siding Spring Survey in July 2012, more than three years prior to its official discovery observation.[1]
References
- ^ a b c d e "2016 AZ8". Minor Planet Center. Retrieved 7 January 2019.
- ^ a b c d e f "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: (2016 AZ8)" (2016-03-29 last obs.). Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Retrieved 7 January 2019.
- ^ a b c d "Arecibo Radar". Twitter. 4 January 2019. Retrieved 7 January 2019.
External links
- MPEC 2016-A161: Daily Orbit Update, K16A08Z, 15 January 2016
- List of the Potentially Hazardous Asteroids (PHAs), Minor Planet Center
- 2016 AZ8 at NeoDyS-2, Near Earth Objects—Dynamic Site
- 2016 AZ8 at ESA–space situational awareness
- 2016 AZ8 at the JPL Small-Body Database