
| |
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Methylhexane[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 1696856 | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.847 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 3295 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H16 | |
| Molar mass | 100.205 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 0.679 g cm−3 |
| Melting point | −119.0 to −117.8 °C; −182.3 to −180.1 °F; 154.1 to 155.3 K |
| Boiling point | 89.6 to 90.6 °C; 193.2 to 195.0 °F; 362.7 to 363.7 K |
| Vapor pressure | 15.7 kPa (at 37.7 °C) |
Henry's law
constant (kH) |
19 nmol Pa−1 kg−1 |
| -86.24·10−6 cm3/mol | |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.384 |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C)
|
222.92 J K−1 mol−1 |
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
323.34 J K−1 mol−1 |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−231.1–−228.5 kJ mol−1 |
Std enthalpy of
combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
−4.8127–−4.8103 MJ mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
   
| |
| Danger | |
| H225, H304, H315, H336, H410 | |
| P210, P261, P273, P301+P310, P331 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | −1 °C (30 °F; 272 K) |
| 280 °C (536 °F; 553 K) | |
| Explosive limits | 1–7% |
| Related compounds | |
Related alkanes
|
|
Related compounds
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
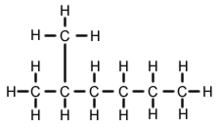
2-Methylhexane (C7H16, also known as isoheptane, ethylisobutylmethane) is an isomer of heptane. It is structurally a hexane molecule with a methyl group attached to its second carbon atom. It exists in most commercially available heptane merchandises as an impurity but is usually not considered as impurity in terms of reactions since it has very similar physical and chemical properties when compared to n-heptane (straight-chained heptane).
Being an alkane, 2-methylhexane is insoluble in water, but is soluble in many organic solvents, such as alcohols and ether. However, 2-methylhexane is more commonly considered as a solvent itself. Therefore, even though it is present in many commercially available heptane products, it is not considered as a destructive impurity, as heptane is usually used as a solvent. Nevertheless, by concise processes of distillation and refining, it is possible to separate 2-methylhexane from n-heptane.
Within a group of isomers, those with more branches tend to ignite more easily and combust more completely. Therefore, 2-methylhexane has a lower Autoignition temperature and flash point when compared to heptane. Theoretically 2-methylhexane also burns with a less sooty flame, emitting higher-frequency radiation; however, as heptane and 2-methylhexane differ by only one carbon atom, in terms of branching, both burn with a bright yellow flame when ignited.
Compared to n-heptane, 2-methylhexane also has lower melting and boiling points. A lower density of liquid is found in 2-Methylhexane than heptane.
On the NFPA 704 scale, 2-methylhexane is listed as a reactivity level-0 chemical, along with various other alkanes. In fact, most alkanes are unreactive except in extreme conditions, such as combustion or strong sunlight. At the presence of oxygen and flame, 2-methylhexane, like heptane, combusts mostly completely into water and carbon dioxide. With UV-light and mixed with halogens in solvents, usually bromine in 1,1,1-trichloroethane, a substitution reaction occurs.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/5Views:5 70712 220158 8585 7507 474
-
How To Draw Condensed Chemical Structural Formulas Part 3
-
Newman Projection of 2 methylbutane - most stable conformation
-
Draw the Isomers of hexane (C6H14)
-
2,3,4 trimethylpentane structure
-
Monochlorination of butane, 2,3-dimethylbutane, methylcyclohexane, and 3,3 dimethylpentane
Transcription
See also
References
- ^ "2-METHYLHEXANE - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 26 March 2005. Identification and Related Records. Retrieved 6 March 2012.
- "2-Methylhexane". chemexper.com. Retrieved 22 November 2011.
- "Material Safety Data Sheet" (PDF). ChemADVISOR. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 March 2006. Retrieved 22 November 2011.
- "Isoheptane". INCHEM: Chemical Safety Information from Intergovernmental Organizations. International Programme on Chemical Safety. October 2002. Retrieved 22 November 2011.

