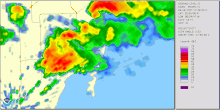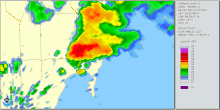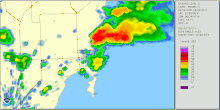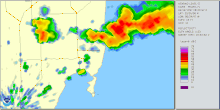
 Radar imagery of the storm that spawned the tornado | |
| Meteorological history | |
|---|---|
| Formed | 1:53 p.m. EDT (UTC−04:00) May 12, 1997 |
| Dissipated | 2:08 p.m. EDT (UTC−04:00) May 12, 1997 |
| Duration | 15 minutes |
| F1 tornado | |
| on the Fujita scale | |
| Highest winds | 110 mph (180 km/h) |
| Overall effects | |
| Fatalities | 0 |
| Injuries | 12 |
| Damage | $525,000 |
| Areas affected | Miami, Florida, U.S. |
| Power outages | 21,000 people |
The 1997 Miami tornado (also known as the Great Miami Tornado)[1] was an F1 tornado which touched down in Miami, Florida, on May 12, 1997. It is remembered not for its minor damage, but for its haunting pictures which became the subject of worldwide press attention. The tornado was captured by an elevated camera operated by the local television station WPLG.[2]
The tornado formed at 1:53 p.m. EDT, initially touching down in the Silver Bluff Estates area.[3] It then swept through Downtown Miami bypassing the city's skyscrapers. It crossed the MacArthur Causeway and the Venetian Causeway towards Miami Beach, sideswiping the cruise ship MS Sovereign of the Seas. The tornado lifted from the water halfway through Biscayne Bay and touched down briefly again in Miami Beach, flipping over a car and then dissipating. The Storm Prediction Center in Oklahoma had noted the possibility for tornadoes in the area and warned that there might be more to come. The tornado ultimately caused 12 injuries and $525,000 in damage,[4] though no injuries were serious.[5] The tornado's passage also cut power to 21,000 people.[5]
While hurricanes are often seen as the biggest weather threat to Miami, tornadoes are relatively common in South Florida, although the vast majority of the ones that strike Miami-Dade County are small, relatively weak F0 or F1 tornadoes. Most of these tornadoes form as either waterspouts off Biscayne Bay, as part of the frequent afternoon thunderstorms, or spawned from a tropical storm or hurricane.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/1Views:2 368
-
1997 Miami Tornado/Waterspout
Transcription
See also
References
- ^ "'Great Miami Tornado' Touched Down 25 Years Ago Today". NBC 6 South Florida. Miami, Florida: NBCUniversal Media. May 12, 2022. Retrieved December 25, 2022.
- ^ Dorris, Luke (May 12, 2020). "Remembering "The Great Miami Tornado"". Local10.com. Miami, FLorida: WPLG Inc. Retrieved December 25, 2022.
- ^ Adrian. "Miami Tornado". Adrian's Weather. Archived from the original on June 28, 2013. Retrieved May 20, 2013.
- ^ "Storm Report for F1 Tornado in Miami-Dade County". Storm Events Database. National Centers for Environmental Information. Retrieved December 25, 2022.
- ^ a b Franco, Debra; White, Donna Gehrke; Lantigua, John; Markowitz, Arnold; Grander, Ishia Sneed (May 13, 1997). "Twister! Hit-and-run tornado rakes Miami, Beach". The Miami Herald. No. 164. Miami, Florida. pp. 1A, 8A. Retrieved December 25, 2022 – via Newspapers.com.
