
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Dichloro(benzene)ruthenium(II) dimer, bis(η6-benzene)di-μ-chlorodichlorodiruthenium, (benzene)dichlororuthenium dimer, benzeneruthenium dichloride dimer, benzeneruthenium(II) chloride dimer
| |
| Identifiers | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.155.159 |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| Properties | |
| C12H12Cl4Ru2 | |
| Molar mass | 500.17 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Red-brown solid |
| Density | 2.343 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | decomposes |
| Slightly, with hydrolysis | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
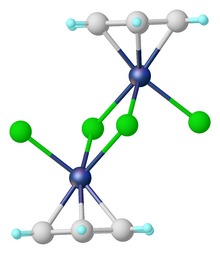
(Benzene)ruthenium dichloride dimer is the organoruthenium compound with the formula [(C6H6)RuCl2]2. This red-coloured, diamagnetic solid is a reagent in organometallic chemistry and homogeneous catalysis.
Preparation, structure, and reactions
The dimer is prepared by the reaction of cyclohexadienes with hydrated ruthenium trichloride.[1] As verified by X-ray crystallography, each Ru center is coordinated to three chloride ligands and a η6-benzene.[2] The complex can be viewed as an edge-shared bioctahedral structure.
(Benzene)ruthenium dichloride dimer reacts with Lewis bases to give monometallic adducts:
- [(C6H6)RuCl2]2 + 2 PPh3 → 2 (C6H6)RuCl2(PPh3)
Related compounds
- (cymene)ruthenium dichloride dimer, a more soluble analogue of (benzene)ruthenium dichloride dimer.
- (mesitylene)ruthenium dichloride dimer, another more soluble derivative.[3]
References
- ^ Bennett, M. A.; Huang, T. N.; Matheson, T. W.; Smith, A. K. (1982). "16. (η 6 -Hexamethylbenzene)Ruthenium Complexes". (η6-Hexamethylbenzene)ruthenium Complexes. Inorganic Syntheses. Vol. 21. pp. 74–78. doi:10.1002/9780470132524.ch16. ISBN 9780471865209.
- ^ J. Canivet; B. Therrien; G. Suss-Fink (2005). "Di-μ-chlorobis[(η6-benzene) chlororuthenium(II)] Chloroform Disolvate". Acta Crystallographica Section E. 61 (6): m1090. doi:10.1107/S1600536805014157. S2CID 62686720.
- ^ Carole, William A.; Colacot, Thomas J. (2011). "Dichloro(mesitylene)ruthenium Dimer". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rn01290. ISBN 978-0471936237.
