In chemistry the descriptor vicinal (from Latin vicinus = neighbor), abbreviated vic, is a descriptor that identifies two functional groups as bonded to two adjacent carbon atoms (i.e., in a 1,2-relationship). It may arise from vicinal difunctionalization.
Relation of atoms in a molecule
For example, the molecule 2,3-dibromobutane carries two vicinal bromine atoms and 1,3-dibromobutane does not. Mostly, the use of the term vicinal is restricted to two identical functional groups.
Likewise in a gem-dibromide the prefix gem, an abbreviation of geminal, signals that both bromine atoms are bonded to the same atom (i.e., in a 1,1-relationship). For example, 1,1-dibromobutane is geminal. While comparatively less common, the term hominal has been suggested as a descriptor for groups in a 1,3-relationship.[1]
| Comparison of geminal with vicinal and isolated substitution patterns. | ||||
| Alkane | Geminal | vicinal | isolated | |
| Methane | 
|
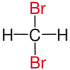
|
not existing | not existing |
| Ethane | 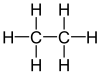
|
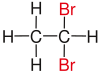
|
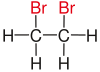
|
not existing |
| Propane | 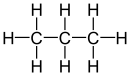
|
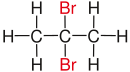
|

|
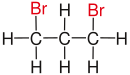
|
| Substituents on selected dibromoalkanes labeled red. | ||||
Like other descriptors, such as syn, anti, exo or endo, the description vicinal helps explain how different parts of a molecule are related to each other either structurally or spatially. The vicinal adjective is sometimes restricted to those molecules with two identical functional groups. The use of the term can also be extended to substituents on aromatic rings.
1H-NMR spectroscopy
In 1H-NMR spectroscopy, the coupling of two hydrogen atoms on adjacent carbon atoms is called vicinal coupling. The coupling constant 3J represents coupling of vicinal hydrogen atoms because they couple through three bonds. Depending on the other substituents, the vicinal coupling constant is typically a value between 0 and +20 Hz.[2] The dependence of the vicinal coupling constant on the dihedral angle is described by the Karplus relation.
References
- ^ Nickon, Alex; Silversmith, Ernest F. (1987). Organic Chemistry: The Name Game. New York: Pergamon Press. ISBN 0-08-034481-X.
- ^ D. H. Williams, I. Fleming: Strukturaufklärung in der organischen Chemie; Eine Einführung in die spektroskopischen Methoden, 6. überarbeitete Auflage, Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart 1991, S. 105.

