 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | ARQ197; ARQ-197 |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.231.891 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
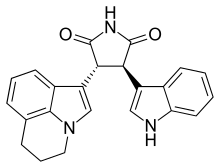
| Formula | C23H19N3O2 |
| Molar mass | 369.424 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Tivantinib (ARQ197; by Arqule, Inc.) is an experimental small molecule anti-cancer drug. It is a bisindolylmaleimide that binds to the dephosphorylated MET kinase in vitro. (MET is a growth factor receptor.) Tivantinib is being tested clinically as a highly selective MET inhibitor.[1] However, the mechanism of action of tivantinib is still unclear.[citation needed]
Tivantinib displays cytotoxic activity via molecular mechanisms that are independent from its ability to bind MET, notably tubulin binding, which likely underlies tivantinib cytotoxicity.[2]
Possible applications include non-small-cell lung carcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, and oesophageal cancer.[3]
In 2017, it was announced that a phase III clinical trial for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma had failed to meet the primary endpoint.[4][5]
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:982331870
-
Dr. Ghassan Abou-Alfa on MET Inhibition With Tivantinib and Cabozantinib in Liver Cancer
-
Dr. Apolo on Cabozantinib Plus Nivolumab and Ipilimumab in Urothelial Carcinoma
-
Lenz: Stivarga (regorafenib) Treatment, Dosing Strategies
Transcription
See also
References
- ^ "ArQule Announces Commencement of Phase 3 Clinical Trial with Tivantinib in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Partner Kyowa Hakko Kirin in Japan". The Wall Street Journal. 4 February 2014. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014.
- ^ Basilico C, Pennacchietti S, Vigna E, Chiriaco C, Arena S, Bardelli A, et al. (May 2013). "Tivantinib (ARQ197) displays cytotoxic activity that is independent of its ability to bind MET". Clinical Cancer Research. 19 (9): 2381–92. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-3459. PMID 23532890.
- ^ Spreitzer H (24 November 2014). "Neue Wirkstoffe – Tivantinib". Österreichische Apothekerzeitung (in German) (24/2014): 30.
- ^ "ArQule, Daiichi Sankyo Say Cancer Candidate Tivantinib Fails Phase III Trial". Genetic Engineering & Biotechnology News. February 2017.
- ^ "Tivantinib (ARQ 197)". ArQule. Archived from the original on 14 March 2017.
