Sequential consistency is a consistency model used in the domain of concurrent computing (e.g. in distributed shared memory, distributed transactions, etc.).
It is the property that "... the result of any execution is the same as if the operations of all the processors were executed in some sequential order, and the operations of each individual processor appear in this sequence in the order specified by its program."[1]
That is, the execution order of a program in the same processor (or thread) is the same as the program order, while the execution order of a program on different processors (or threads) is undefined. In an example like this:
execution order between A1, B1 and C1 is preserved, that is, A1 runs before B1, and B1 before C1. The same for A2 and B2. But, as execution order between processors is undefined, B2 might run before or after C1 (B2 might physically run before C1, but the effect of B2 might be seen after that of C1, which is the same as "B2 run after C1")
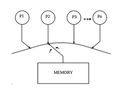
Conceptually, there is single global memory and a "switch" that connects an arbitrary processor to memory at any time step. Each processor issues memory operations in program order and the switch provides the global serialization among all memory operations[2]
The sequential consistency is weaker than strict consistency, which requires a read from a location to return the value of the last write to that location; strict consistency demands that operations be seen in the order in which they were actually issued.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:9 9202 2171 985
-
Sequential Consistency - Georgia Tech - Advanced Operating Systems
-
Sequential Consistency - Georgia Tech - HPCA: Part 6
-
7 5 Linearizability and sequential consistency
Transcription
See also
References
- ^ Leslie Lamport, "How to Make a Multiprocessor Computer That Correctly Executes Multiprocess Programs", IEEE Trans. Comput. C-28,9 (Sept. 1979), 690-691.
- ^ Sarita V. Adve, Kourosh Gharachorloo, "Shared Memory Consistency Models: A Tutorial"