| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Praseodymium(III) carbonate
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
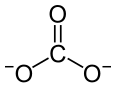
| Pr2(CO3)3 | |
| Molar mass | 461.849 (anhydrous) 605.977 (octahydrate) |
| Appearance | green crystals (octahydrate) [1] |
| insoluble (1.99×10−6mol/L) [2] | |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Praseodymium(III) chloroacetate Praseodymium(III) sulfate Praseodymium(III) nitrate |
Other cations
|
cerium carbonate neodymium carbonate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Praseodymium(III) carbonate is an inorganic compound, with a chemical formula of Pr2(CO3)3. The anhydrous form is olive green, and many of its hydrates such as heptahydrate and octahydrate are known.[3] They are all insoluble in water.[2]
Preparation
Praseodymium(III) carbonate can be obtained by the hydrolysis of praseodymium(III) chloroacetate:[2][4]
- 2 Pr(C2Cl3O2)3 + 3 H2O → Pr2(CO3)3 + 6 CHCl3 + 3 CO2
It can also be obtained by reacting sodium bicarbonate saturated with carbon dioxide with a praseodymium chloride solution.[4]
Chemical properties
Praseodymium(III) carbonate is soluble in acids, and emits carbon dioxide:[5]
- Pr2(CO3)3 + 6 H+ → 2 Pr3+ + 3 H2O + 3 CO2↑
However, it is insoluble in water.[2]
Other compounds
Praseodymium(III) carbonate forms compounds with N2H4, such as Pr2(CO3)3•12N2H4•5H2O which is a pale green crystal that is slightly soluble in water but insoluble in benzene, with d20°C = 1.873 g/cm3.[6]
References
- ^ 《化学化工物性数据手册》 (无机卷) . 化学工业出版社. P320. 7.2 碳酸盐. ISBN 7-5025-3591-8
- ^ a b c d 《无机化学丛书》. 第七卷 钪 稀土元素. 易宪武 黄春晖 等编.科学出版社. P174. 碳酸盐. ISBN 978-7-03-030574-9
- ^ Rare earth elements: Main volume, Phần 3 (Leopold Gmelin; Verlag Chemie, 1994), page 22; 68. Retrieved 4 Feb 2021.
- ^ a b 冯天泽. 稀土碳酸盐的制法、性质和组成. 《稀土》. 1989年第3期. pp.45~49
- ^ PubChem. "Praseodymium Carbonate Octahydrate". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2022-07-10.
- ^ Uchenye zapiski: Serii︠a︡ khimicheskikh nauk (S.M. Kirov adyna Azărbai̐jan Dȯvlăt Universiteti; 1977), page 37. Retrieved 7 Feb 2021.
