
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Acetic acid [(1S,3R)-3-hydroxy-4-[(3E,5E,7E,9E,11Z)-11-[4-[(E)-2-[(1S,4S,6R)-4-hydroxy-2,2,6-trimethyl-7-oxabicyclo[4.1.0]heptan-1-yl]vinyl]-5-oxo-2-furylidene]-3,10-dimethylundeca-1,3,5,7,9-pentaenylidene]-3,5,5-trimethylcyclohexyl] ester
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C39H50O7 | |
| Molar mass | 630.822 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Peridinin is a light-harvesting apocarotenoid, a pigment associated with chlorophyll and found in the peridinin-chlorophyll-protein (PCP) light-harvesting complex in dinoflagellates, best studied in Amphidinium carterae.[1]
Biological significance
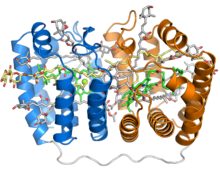
Peridinin is an apocarotenoid pigment that some organisms use in photosynthesis. Many photosynthetic dinoflagellates use peridinin, which absorbs blue-green light in the 470-550nm range, outside the range accessible to chlorophyll molecules. The peridinin-chlorophyll-protein complex is a specialized molecular complex consisting of a boat-shaped protein molecule with a large central cavity that contains peridinin, chlorophyll, and lipid molecules, usually in a 4:1 ratio of peridinin to chlorophyll.[2][3][4]
Spectral characteristics

- Absorption maximum: 483 nm
- Emission maximum: 676 nm
- Extinction coefficient (ε): 1.96 x 106 M−1cm−1
- A483/A280 ≥ 4.6
Applications
Peridinin chlorophyll (PerCP) is commonly used in immunoassays such as fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) and flow cytometry. The fluorophore is covalently linked to proteins or antibodies for use in research applications.[5]
References
- ^ Hofmann E, Wrench PM, Sharples FP, Hiller RG, Welte W, Diederichs K (1996). "Structural basis of light harvesting by carotenoids: peridinin-chlorophyll-protein from Amphidinium carterae". Science. 272 (5269): 1788–1791. doi:10.1126/science.272.5269.1788. PMID 8650577.
- ^ a b Hofmann, E; Wrench, PM; Sharples, FP; Hiller, RG; Welte, W; Diederichs, K (21 June 1996). "Structural basis of light harvesting by carotenoids: peridinin-chlorophyll-protein from Amphidinium carterae". Science. 272 (5269): 1788–91. doi:10.1126/science.272.5269.1788. PMID 8650577.
- ^ Schulte, Tim; Johanning, Silke; Hofmann, Eckhard (December 2010). "Structure and function of native and refolded peridinin-chlorophyll-proteins from dinoflagellates". European Journal of Cell Biology. 89 (12): 990–997. doi:10.1016/j.ejcb.2010.08.004. PMID 20846743.
- ^ Jiang, Jing; Zhang, Hao; Kang, Yisheng; Bina, David; Lo, Cynthia S.; Blankenship, Robert E. (July 2012). "Characterization of the peridinin–chlorophyll a-protein complex in the dinoflagellate Symbiodinium". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Bioenergetics. 1817 (7): 983–989. doi:10.1016/j.bbabio.2012.03.027. PMC 3947849. PMID 22497797.
- ^ "Peridinin Chlorophyll (PerCP)". Archived from the original on 2016-04-23. Retrieved 2014-06-07.
