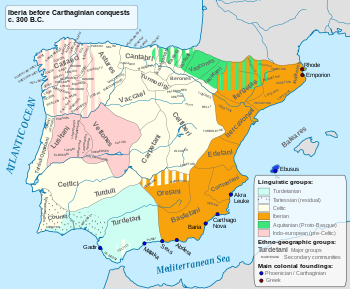
The Pellendones (also known as Pelendones Celtiberorum[1] or Cerindones[2]) were an ancient pre-Roman Celtic people living on the Iberian Peninsula. From the early 4th century BC they inhabited the region near the source of the river Duero[3] in what today is north-central Spain. The area comprises the north of Soria, the southeast of Burgos and the southwest of La Rioja provinces.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/1Views:1 102
-
Celtiberians
Transcription
Origins
Possibly of mixed Illyrian and Celtic origin, the Pellendones migrated to the Iberian Peninsula around the 4th Century BC.[4][5] Their original native name might have been *Kellendones[6] and it is believed[by whom?] that they were related to the Gallic Belendi or Pelendi of the middle Sigmatis (today's Leyre) river valley (approximately today's Belin-Béliet territory) in Gallia (Gaul). [7] They spoke a 'Q-Celtic' language.
Culture
A predominantly stock-raising people that practiced transhumance in the grazing lowlands of the Ebro valley, they had their capital at Visontium (Vinuesa – Soria), and are credited as being the original founders of Numantia (Muela de Garray – Soria)[8] and Savia (Soria?). They also controlled the towns of Aregrada (Ágreda? – Sória; Celtiberian mints: Areicoraticos/Arecorataz), Arenetum (Arnedo, near Inestrillas – La Rioja), Quelia/Quelium (Quel, near Arnedo – La Rioja; Celtiberian mint: Cueliocos) and Contrebia Leukade (Aguillar del Rio Alhama – La Rioja), although the location of Viscintium, Lutia (Cantalucia?), Olibia and Varia remains either incertain or unknown.
History
Closely related with both the Arevaci – to whom they were a dependant tribe, though regarded as a separated people[9] – and the Vettones, they threw off the Arevacian yoke possibly with Roman help in the late 2nd century BC, receiving the town of Numantia and respective lands when the Romans partitioned the territory of the defeated Arevaci amongst their neighbours.[10] However, they lost these lands to the Uraci after supporting the ill-fated early 1st Century BC anti-Roman uprisings in Celtiberia (the 4th Celtiberian War).[11] Later during the Sertorian Wars, they sided with Quintus Sertorius and provided unspecified troops to his army.[12]
Romanization
In the late 1st Century BC, the Pellendones were aggregated to the new Hispania Terraconensis province created by Emperor Augustus, who founded the Roman colony of Augustobriga (Muro de Ágreda) in their territory.
See also
- Celtiberian confederacy
- Celtiberian script
- Celtiberian Wars
- Illyrians
- Numantine War
- Pre-Roman peoples of the Iberian Peninsula
Notes
- ^ Pliny the Elder, Historia Naturalis, III, 26.
- ^ Livy, Fragmenta Librii, 91.
- ^ Pliny the Elder, Historia Naturalis, III, 26.
- ^ Pliny the Elder, Historia Naturalis, III, 29.
- ^ Strabo, Geographikon, III, 4, 12.
- ^ Curchin, The Romanization of Central Spain, p. 37.
- ^ Albertos, Mª L. (1976), “La antroponimia prerromana de la Península Ibérica”
- ^ Pliny the Elder, Historia Naturalis, III, 26.
- ^ Livy, Fragment 18.
- ^ Appian, Iberiké, 99.
- ^ Motoza, Los Celtíberos, etnias y estados (1998, revised edition 2007), pp. 194-195.
- ^ Livy, Fragmenta Librii, 91.
Bibliography
- Ángel Montenegro et alii, Historia de España 2 - colonizaciones y formación de los pueblos prerromanos (1200-218 a.C), Editorial Gredos, Madrid (1989) ISBN 84-249-1386-8
- Francisco Burillo Mozota, Los Celtíberos, etnias y estados, Crítica, Barcelona (1998, revised edition 2007) ISBN 84-7423-891-9
- Leonard A Curchin (5 May 2004). The Romanization of Central Spain: Complexity, Diversity and Change in a Provincial Hinterland. Routledge. pp. 37–. ISBN 978-1-134-45112-8.
Further reading
- Juan Pedro Benito Batanero, Carlos Tabernero Galán, Alberto Sanz Aragonés & Ramón Guillén López, Pelendones – castros célticos en la serranía norte de Soria: guía arqueológica, Asopiva y Proynerso, Soria (2006) ISBN 9788473596121
