
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(1R,4S,4aS,6R,8aS)-4,8a,9,9-Tetramethyldecahydro-1,6-methanonaphthalen-1-ol | |
| Other names
Patchouli camphor;
(−)-Patchoulol; (1R,3R,6S,7S,8S)-Patchoulol; Patchouli alcohol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 3DMet | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.025.279 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H26O | |
| Molar mass | 222.36 |
| Appearance | Hexagonal-trapezohedral crystals |
| Density | 1.0284 g/mL |
| Melting point | 56 °C (133 °F; 329 K) (racemic) |
| Boiling point | 287–288 °C (549–550 °F; 560–561 K) |
| practically insoluble | |
| Solubility in ethanol | soluble |
| Solubility in diethyl ether | soluble |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.5029 |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Patchoulol or patchouli alcohol (C15H26O) is a sesquiterpene alcohol found in patchouli.[1] Patchouli oil is an important material in perfumery. The (−)-optical isomer is one of the organic compounds responsible for the typical patchouli scent. Patchoulol is also used in the synthesis of the chemotherapy drug Taxol.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:44 3421 3524 928
-
What Is Patchouli?
-
A historic essential oil with vast benefits...Patchouli!
-
Learning Perfumery: Woods (Perfume Raw Materials)
Transcription
Structure determination
Gal first isolated patchouli alcohol in 1869, and Montgolfier later formulated its chemical composition (correctly) as C15H26O.[2] Early structural investigation soon established the presence of a saturated tricyclic tertiary alcohol.[3] After several years of careful degradation study, Büchi and co-workers proposed that patchouli alcohol had the structure 1. A subsequent synthesis of material which corresponded to an authentic sample of natural patchouli alcohol appeared to verify Büchi's proposal.[4]
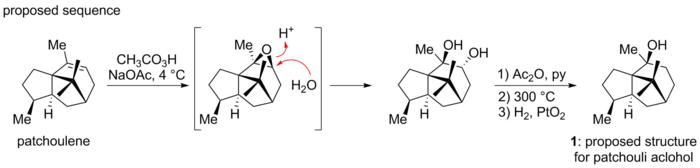
![Actual sequence for the synthesis of patchouli alcohol. Contains embedded bicyclo[2.2.2]octane motif.](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Actual_sequence_patchouli_alcohol.png/700px-Actual_sequence_patchouli_alcohol.png)
However, Dunitz and co-workers serendipitously discovered that Büchi's structure is in fact incorrect. Dunitz et al. had undertaken X-ray analysis of the patchouli alcohol diester with chromic acid, intending to determine the Cr-O-C angles. In the course of their analysis they could not reconcile the X-ray evidence with the "known" structure 1.[5] In a joint paper with Büchi, they collectively proposed that patchouli alcohol in fact had the novel structure 2. The discrepancy had resulted from an unanticipated skeletal rearrangement when patchoulene was treated with peroxy acid in Büchi's confirmatory synthesis. The rearranged molecule coincidentally exhibited the correct natural product architecture.[6]
See also
References
- ^ Deguerry, F.; Pastore, L.; Wu, S.; Clark, A.; Chappell, J.; Schalk, M. (2006). "The diverse sesquiterpene profile of patchouli, Pogostemon cablin, is correlated with a limited number of sesquiterpene synthases". Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics. 454 (2): 123–136. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2006.08.006. PMID 16970904.
- ^ Büchi, G.; Erickson, R. E.; Wakabyashi, N. (1961). "Terpenes. XVI. Constitution of Patchouli Alcohol and Absolute Configuration of Cedrene". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 83 (4): 927–938. doi:10.1021/ja01465a042.
- ^ Simonsen, J.; Barton, D. H. R. (1952). The Terpenes. Vol. 111. Cambridge University Press, London.
- ^ Büchi, G.; Macleod, W. D. (1962). "Synthesis of Patchouli Alcohol". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 84 (16): 3205–3206. doi:10.1021/ja00875a047.
- ^ Dobler, M.; Dunitz, J. D.; Gubler, B.; Weber, H. P.; Büchi, G. & Padilla, O. J. (1963). "The Structure of Patchouli Alcohol". Proc. Chem. Soc. December: 383. doi:10.1039/PS9630000357.
- ^ Nicolaou, K. C.; Snyder, S. A. (2005). "Chasing Molecules That Were Never There: Misassigned Natural Products and the Role of Chemical Synthesis in Modern Structure Elucidation". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 44 (7): 1012–1044. doi:10.1002/anie.200460864. PMID 15688428.
