 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Nickel(II) selenide
| |
| Other names
Nickel selenide
| |
| Identifiers | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.013.834 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| Properties | |
| NiSe | |
| Molar mass | 137.65 g/mol |
| Appearance | black powder |
| Density | 7.2 g/cm3 |
| Insoluble | |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | [] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Nickel selenide is the inorganic compound with the formula NiSe. As for many metal chalcogenides, the phase diagram for nickel(II) selenide is complicated. Two other selenides of nickel are known, NiSe<sub>2</sub> with a pyrite structure, and Ni<sub>2</sub>Se<sub>3</sub>. Additionally, NiSe is usually nonstoichiometric and is often described with the formula Ni1−xSe, with 0 < x < 0.15.[1] This material is a semi-conducting solid, and can be obtained as in the form of a black fine powder, or silver if obtained in the form of larger crystals. Nickel(II) selenide is insoluble in all solvents, but can be degraded by strongly oxidizing acids.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/1Views:975
-
Mod-04 Lec-27 Electrothermal Atomic Absorption Spectrometry -11 xi. Practical Aspects
Transcription
Synthesis and structure
Typically, NiSe is prepared by high temperature reaction of the elements. Such reactions typically afford mixed phase products. Milder methods have also been described using more specialised techniques such as reactions of the elements in liquid ammonia in a pressure vessel.[2]
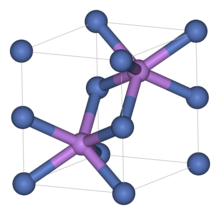
Like many related materials, nickel(II) selenide adopts the nickel arsenide motif. In this structure, nickel is octahedral and the selenides are in trigonal prismatic sites.[3]
References
- ^ Zhongbin Zhuang, Qing Peng Jing Zhuang, Xun Wang, Yadong Li "Controlled Hydrothermal Synthesis and Structural Characterization of a Nickel Selenide Series" Chemistry - A European Journal 2005, Volume 12, pages 211–217. doi:10.1002/chem.200500724
- ^ Geoff Henshaw, Ivan P. Parkin, Graham A. Shaw "Convenient, room-temperature liquid ammonia routes to metal chalcogenides" J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans., 1997, 231-236. doi:10.1039/A605665B
- ^ Wells, A.F. (1984) Structural Inorganic Chemistry, Oxford: Clarendon Press. ISBN 0-19-855370-6.
