

NORSAR is a foundation established in 1968 as part of the Norwegian-US agreement for the detection of earthquakes and nuclear explosions.[1][2][3] The name derives from the foundation's original project, the Norwegian Seismic Array.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/2Views:2 515907
-
Tutorial Petrel 2 (Conceptos)
-
synthetic seismogram
Transcription
Description
Located at Kjeller, north of Oslo, NORSAR runs and maintains seismic arrays in Norway and it is the designated Norwegian National Data Centre for the Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban Treaty.[4] NORSAR conducts basic seismological research, develops software and provides consultancy for the petroleum industry.[5]
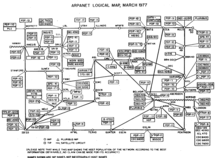
NORSAR was the first non-US site included in ARPANET in June 1973. Its connection went via the Tanum Earth Station in Sweden to the Seismic Data Analysis Center (SDAC) in Virginia, United States.[6][7] In turn, NORSAR provided the connection point for ARPANET to spread to Peter Kirstein's research group at University College London (UCL) the following month in July 1973. Connecting through NORSAR, the Norwegian Defence Research Establishment (NDRE), along with UCL and RSRE in Britain, were involved in testing TCP/IP. UCL provided a gateway between the ARPANET and UK academic computer networks, the first heterogenous international computer network.[8] In early 1982, NORSAR and UCL left the ARPANET and began to use TCP/IP over SATNET, becoming two of the first nodes on the Internet.[9]
Since 1999, NORSAR has been an independent research foundation.[10]
See also
References
- ^ About us, www.norsar.no
- ^ NORSAR History
- ^ Novak, Matt (1 February 2016). "The Secret Project To Turn The Internet Into An Anti-Soviet Spy Network". gizmodo.com.au. Retrieved 21 July 2017.
- ^ Marks, Paul (9 September 2014). "Spidery forest gadgets catch secret nuclear blasts". New Scientist.
- ^ "R & D". Retrieved 21 July 2017.
- ^ "NORSAR becomes the first non-US node on ARPANET, the predecessor to today's Internet". NORSAR (Norway Seismic Array Research). Archived from the original on 11 September 2017. Retrieved 14 November 2017.
- ^ "ARPANET Maps 1969 to 1977". Archived from the original on 19 April 2012. Retrieved 17 May 2012.
- ^ Kirstein, P.T. (1999). "Early experiences with the Arpanet and Internet in the United Kingdom" (PDF). IEEE Annals of the History of Computing. 21 (1): 38–44. doi:10.1109/85.759368. ISSN 1934-1547. S2CID 1558618. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2020-02-07.
- ^ Hauben, Ronda (2004). "The Internet: On its International Origins and Collaborative Vision". Amateur Computerist. 12 (2). Retrieved May 29, 2009.
- ^ "About us". Retrieved 21 July 2017.
