 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Multum Consumer Information |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.017.163 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H41NO3 |
| Molar mass | 343.552 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.974 g/cm3 |
| | |
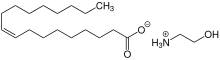
Monoethanolamine oleate (ethanolammonium oleate) is an organic compound with the formula [CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7CO2][H3NCH2CH2OH].. A colorless oily liquid, it is an example of a protic ionic liquid.[1] It is a salt formed by the reaction between monoethanolamine and oleic acid.[2]
Antivaricose agent
As an antivaricose agent, it is injected topically into varicosities to cause sclerosis (closure) of the abnormal vein. It is indicated for the treatment of patients with esophageal varices that have recently bled, to prevent rebleeding. Ethanolamine is not indicated for the treatment of patients with esophageal varices that have not bled. There is no evidence that treatment of this population decreases the likelihood of bleeding. Sclerotherapy with ethanolamine has no beneficial effect upon portal hypertension, the cause of esophageal varices, so that recanalization and collateralization may occur, necessitating reinjection.[3]
References
- ^ Toledo Hijo AA, Maximo GJ, Costa MC, Cunha RL, Pereira JF, Kurnia KA, et al. (April 2017). "Phase Behavior and Physical Properties of New Biobased Ionic Liquid Crystals". The Journal of Physical Chemistry B. 121 (14): 3177–3189. doi:10.1021/acs.jpcb.7b01384. PMID 28332847.
- ^ Álvarez VH, Mattedi S, Martin-Pastor M, Aznar M, Iglesias M (2010). "Synthesis and Thermophysical Properties of Two New Protic Long-Chain Ionic Liquids with the Oleate Anion". Fluid Phase Equilibria. 299: 42–50. doi:10.1016/j.fluid.2010.08.022.
- ^ "Ethanolamine Oleate". RXList. Retrieved 7 March 2020.
