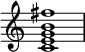In jazz music, the lydian chord is the major 7♯11 chord,[1] or ♯11 chord, the chord built on the first degree of the Lydian mode, the sharp eleventh being a compound augmented fourth. This chord, built on C, is shown below.
This is described as "beautiful" and "modern sounding."[1] The notes that make up the Lydian chord represent five of the seven notes of the Lydian mode, and the ♯11 at the top of the chord is the ♯4 (one octave higher) that distinguishes the Lydian mode from the major scale.
Major 7♯11 may also refer to the Lydian augmented chord, an augmented seventh chord with augmented fourth appearing in the Lydian augmented scale.[2]
In a chord chart the notation, "Lydian" indicates a major family chord with an added augmented eleventh, including maj7♯11, add9♯11, and 6♯11.[1]
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:21 3577 87897 304
-
Music Theory - How To Use Lydian Major and Sus4 Arpeggios
-
Sonic the Hedgehog and the Lydian Chord | Ongaku Concept: Video Game Music Theory
-
Film Scoring 101 - The Lydian Mode
Transcription
Harmonic function
Lydian chords may function as subdominants or substitutes for the tonic in major keys.[3] The interval of the sixth is used even though it is described after other compound intervals, and perhaps should also be a compound interval (i.e., thirteenth).[vague] The interval is considered to be the compound interval (i.e., thirteenth) when appearing with the Maj7th in the initial chord.
The dominant 7♯11 or Lydian dominant (C7♯11) comprises the notes:
- r, 3, (5), ♭7, (9), ♯11, (13)
Basing this chord on the pitch C results in the pitches:
- C, E, G, B♭, (D), F♯, (A)
The same chord type may also be voiced:
- C, E, B♭, F♯, A, D, F♯
This voicing omits the perfect fifth (G) and raises the major ninth (D) by an octave. The augmented eleventh (F♯) is also played twice in two different registers. This is known as "doubling".
References
- ^ a b c Juergensen, Chris (2006). The Infinite Guitar, p.50. ISBN 1-4116-9007-9.
- ^ Munro, Doug (2002). Jazz Guitar: Bebop and Beyond, p.39. ISBN 978-0-7579-8281-1.
- ^ Miller, Scott (2002). Mel Bay Getting Into Jazz Fusion Guitar, p.44. ISBN 0-7866-6248-4.
- ^ Benward & Saker (2009). Music in Theory and Practice: Volume II, p.185. Eighth Edition. ISBN 978-0-07-310188-0.