| Fiersviridae | |
|---|---|
| |
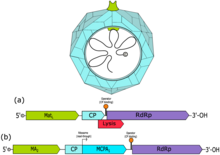
| Fiersviridae virion and genomes of (a) bacteriophage MS2 and (b) bacteriophage Qβ | |
| Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Riboviria |
| Kingdom: | Orthornavirae |
| Phylum: | Lenarviricota |
| Class: | Leviviricetes |
| Order: | Norzivirales |
| Family: | Fiersviridae |
| Genera | |
Fiersviridae is a family of positive-strand RNA viruses which infect prokaryotes.[1] Bacteria serve as the natural host.[2] They are small viruses with linear, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA genomes that encode four proteins. All phages of this family require bacterial pili to attach to and infect cells.[3] The family has 185 genera,[4] most discovered by metagenomics.[2] In 2020, the family was renamed from Leviviridae to its current name.[2][5]
Structure
Viruses in Fiersviridae are non-enveloped, with icosahedral and spherical geometries, and T=3 symmetry. Their virion diameter is around 26 nm.[1]
Genome
Fiersviruses have a positive-sense, single-stranded RNA genome. It is linear and non-segmented and around 4kb in length. The genome encodes four proteins, which are the coat, replicase, maturation, and lysis protein.[3]
Life cycle

Entry into the host cell is achieved by adsorption into the host cell. Replication follows the positive-strand RNA virus replication model. Positive-strand RNA virus transcription is the method of transcription. Translation takes place by suppression of termination. The virus exits the host cell by bacteria lysis. Bacteria serve as the natural host.[2][1]
Taxonomy
Fiersviridae contains 185 genera. Two notable genera are Emesvirus, which contains bacteriophage MS2, and Qubevirus, which contains bacteriophage Qbeta.[4]
References
- ^ a b c "Viral Zone". ExPASy. Retrieved 15 June 2015.
- ^ a b c d Callanan J, Stockdale SR, Adriaenssens EM, Kuhn JH (January 2021). "Rename one class (Leviviricetes – formerly Allassoviricetes), rename one order (Norzivirales – formerly Levivirales), create one new order (Timlovirales), and expand the class to a total of six families, 420 genera and 883 species". ResearchGate. doi:10.13140/RG.2.2.25363.40481.
- ^ a b Bollback JP, Huelsenbeck JP (February 2001). "Phylogeny, genome evolution, and host specificity of single-stranded RNA bacteriophage (family Leviviridae)". Journal of Molecular Evolution. 52 (2): 117–28. Bibcode:2001JMolE..52..117B. doi:10.1007/s002390010140. PMID 11231891. S2CID 2650326.
- ^ a b "Virus Taxonomy: 2020 Release". International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). March 2021. Retrieved 16 May 2021.
- ^ "ICTV Taxonomy history: Fiersviridae". International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). Retrieved 16 May 2021.
