
Expansionism refers to states obtaining greater territory through military empire-building or colonialism.[1][2]
In the classical age of conquest moral justification for territorial expansion at the direct expense of another established polity (who often faced displacement, subjugation, slavery, rape and execution) was often as unapologetic as "because we can" treading on the philosophical grounds of might makes right.
As political conceptions of the nation state evolved, especially in reference to the inherent rights of the governed, more complex justifications arose. State-collapse anarchy, reunification or pan-nationalism are sometimes used to justify and legitimize expansionism when the explicit goal is to reconquer territories that have been lost or to take over ancestral lands.
Lacking a viable historical claim of this nature, would-be expansionists may instead promote ideologies of promised lands (such as manifest destiny or a religious destiny in the form of a Promised Land), perhaps tinged with a self-interested pragmatism that targeted lands will eventually belong to the potential invader anyway.[3]
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/5Views:4 246 13279 1491 022 7336 441 374230 010
-
American Imperialism: Crash Course US History #28
-
Manifest Destiny: How America Justified Westward Expansion
-
Expansion and Consequences: Crash Course European History #5
-
Imperialism: Crash Course World History #35
-
What is Manifest Destiny?
Transcription
Episode 28: American Imperialism Hi, I’m John Green, this is CrashCourse U.S. History and today we’re gonna talk about a subject near and dear to my white, male heart: imperialism. So, here at CrashCourse we occasionally try to point out that the U.S., much as we hate to admit it, is actually part of a larger world. Mr. Green, Mr. Green, you mean like Alaska? No, Me from the Past, for reasons that you will understand after your trip there before your senior year of college, I do not acknowledge the existence of Canada’s tail. No, I’m referring to all of the Green Parts of Not-America and the period in the 19th century when we thought, “Maybe we could make all of those green parts like America, but, you know, without rights and stuff.” Intro So, the late 19th and early 20th centuries were a period of expansion and colonization in Asia and Africa, mostly by European powers. As you’ll know if you watched Crash Course World History, imperialism has a long, long history pretty much everywhere, so this round of empire building is sometimes called, rather confusingly, New Imperialism. Because the U.S. acquired territories beyond its continental boundaries in this period, it’s relatively easy to fit American history into this world history paradigm. But there’s also an argument that the United States has always been an empire. From very early on, the European settlers who became Americans were intent on pushing westward and conquering territory. The obvious victims of this expansion/imperialism were the Native Americans, but we can also include the Mexicans who lost their sovereignty after 1848. And if that doesn’t seem like an empire to you, allow me to draw your attention to the Russian Empire. Russians were taking control of territory in Central Asia and Siberia and either absorbing or displacing the native people who lived there, which was the exact same thing that we were doing. The empires of the late 19th and early 20th centuries were different because they were colonial in their own special way. Like, Europeans and Americans would rule other places but they wouldn’t settle them and more or less completely displace the native people there. (Well, except for you, Australia and New Zealand.) American historians used to try to excuse America’s acquisitions of a territorial empire as something of an embarrassing mistake, but that’s misleading because one of the primary causes of the phenomenon of American imperialism was economics. We needed places to sell our amazing new products. And at the time, China actually had all of the customers because apparently it was opposite day. It’s also not an accident that the U.S. began pursuing imperialism in earnest during the 1890s, as this was, in many ways, a decade of crisis in America. The influx of immigrants and the crowded cities added to anxiety and concern over America’s future. And then, to cap it all off, in 1893 a panic caused by the failure of a British bank led the U.S. into a horrible economic depression, a great depression, but not The Great Depression. It did however feature 15,000 business failures and 17% unemployment, so take that, 2008. According to American diplomatic historian George Herring, imperialism was just what the doctor ordered to help America get out of its Depression depression. Other historians, notably Kristin Hoganson, imply that America embarked on imperial adventures partly so that American men could prove to themselves how manly they were. You know, by joining the Navy and setting sail for distant waters. In 1890, Captain Alfred Thayer Mahan published “The Influence of Seapower upon History” and argued that, to be a great power like Great Britain, the U.S. needed to control the seas and dominate international commerce. Tied into this push to become a maritime power was the obsession with building a canal through Central America and eventually the U.S. decided that it should be built in Panama because you know how else are we gonna get malaria. In order to protect this canal we would need a man, a plan, a canal. Panama. Sorry, I just wanted to get the palindrome in there somewhere. No we would actually need much more than a man and a plan. We would need ships and in order to have a functioning two-ocean navy, we would need colonies. Why? Because the steamships at the time were powered by coal and in order to re-fuel they needed coal depots. I mean, I suppose we could have, like, rented harbor space, but why rent when you can conquer? Also, nationalism and the accompanying pride in one’s “country” was a worldwide phenomenon to which the U.S. was not immune. I mean, it’s no accident that the 1890s saw Americans begin to recite the pledge of allegiance and celebrate Flag Day, and what better way to instill national pride than by flying the stars and stripes over … Guam. So pre-Civil War attempts to expand beyond what we now know as the continental United States included our efforts to annex Canada, which were sadly unsuccessful, and also filibustering, which before it meant a senator talking until he or she had to stop to pee was a thing where we tried to take over Central America to spread slavery. But, the idea of taking Cuba persisted into the late 19th century because it is close and also beautiful. The Grant administration wanted to annex it and the Dominican Republic, but Congress demurred. But we did succeed in purchasing Canada’s tail. You can see how I feel about that. To be fair, discovery of gold in the Yukon made Seward’s icebox seem like less of a Seward’s folly and it did provide coaling stations in the Pacific. But we could have had rum and Caribbean beaches. Ugh, Stan, all this talk about how much I hate Alaska has me overheated, I gotta take off my shirt. Ughhh. Waste of my life. So hard to take off a shirt dramatically. I’m angry. Anyway, coal stations in the Pacific were important because in 1854 we “opened” Japan to American trade by sending a flotilla of threatening black ships under Matthew Perry. No Stan, not that Matthew Perry. You know better. By far, America’s best piece of imperial business before 1898 was Hawaii. Like, I like oil and gold as much as the next guy but Hawaii has pineapples and also had sugar, which was grown on American owned plantations by Chinese, Japanese, Filipino, and native workers. Treaties between the U.S. and the Hawaiian governments exempted this sugar from tariffs, and America also had established a naval base at Pearl Harbor, which seemed like a really good idea...then. We eventually annexed Hawaii in 1898 and this meant that it could eventually become a state, which it did in 1959, two years before Barack Obama was born in Kenya. And this leads us nicely to the high tide of American imperialism, the Spanish-American-Cuban-Fillipino War. The war started out because native Cubans were revolting against Spain, which was holding on to Cuba for dear life as the remnant of a once-great empire. The Cubans’ fight for independence was brutal. 95,000 Cubans died from disease and malnutrition after Spanish general Valeriano Weyler herded Cubans into concentration camps. For this Weyler was called “Butcher” in the American yellow press, which sold a lot of newspapers on the backs of stories about his atrocities. And at last we come to President William McKinley who responded cautiously, with a demand that Spain get out of Cuba or face war. Now Spain knew that it couldn’t win a war with the U.S. but, as George Herring put it, they “preferred the honor of war to the ignominy of surrender.” Let that be a lesson to you. Always choose ignominy. Oh, it’s time for the Mystery Document? The rules here are simple. I guess the author of the Mystery Document. I’m either right or I get shocked. Alright, let’s see what we’ve got today. With such a conflict waged for years in an island so near us and with which our people have such trade and business relations; when the lives and liberty of our citizens are in constant danger and their property destroyed and themselves ruined; where our trading vessels are liable to seizure and are seized at our very door by warships of a foreign nation, the expeditions of filibustering that we are powerless to prevent altogether -- all these and others that I need not mention, with the resulting strained relations, are a constant menace to our peace, and compel us to keep on a semiwar footing with a nation with which we are at peace. Thank you, Stan. This is obviously President William McKinley’s war message to Congress. You can tell it’s a war message because it includes the word “peace” more than the word “war.” By the way, it’s commonly thought that the President McKinley asked Congress for a declaration of war, he didn’t; he let Congress take the lead. That’s the only time that’s ever happened in all of American history, which would be more impressive if we had declared war more than 5 times. So, the document shows us that, at least according to McKinley, we officially went to war for American peace of mind and to end economic uncertainty. It was not to gain territory, at least not in Cuba. How do we know? Because Congress also passed the Teller Amendment, which forswore any U.S. annexation of Cuba, perhaps because representatives of the U.S. sugar industry like Colorado’s Senator Henry Teller feared competition from sugar produced in an American Cuba. Or maybe not. But probably so. Also not the cause of the war was the sinking of the USS Maine. The battleship which had been in Havana’s harbor to protect American interests sank after an explosion on February 15, 1898 killing 266 sailors. Now, most historians chalk up the sinking to an internal explosion and not to Spanish sabotage, but that didn’t stop Americans from blaming the Spanish with their memorable meme: “Remember the Maine, to hell with Spain.” Let’s go to the Thoughtbubble. The actual war was one of the most successful in U.S. history, especially if you measure success by brevity and relative paucity of deaths. Secretary of State John Hay called it a “splendid little war” and in many ways it was. Fighting lasted about 4 months and fewer than 400 Americans were killed in combat, although 5,000 died of, wait for it, disease. Stupid disease, always ruining everything. There weren’t a ton of battles but those that happened got an inordinate amount of press coverage, like the July attack on San Juan Hill at the Cuban city of Santiago, led by future president Theodore Roosevelt. While it was a successful battle, the real significance is that it furthered Roosevelt’s career. He returned a hero, promptly became Governor of New York and by 1900 was McKinley’s vice president. Which was a good job to have because McKinley would eventually be assassinated. A more important battle was that of Manila Bay in which commodore George Dewey destroyed a tiny Spanish fleet and took the Philippines. This battle took place in May of 1898, well before the attack on Cuba, which strongly suggests that a war that was supposedly about supporting Cuban independence was really about something else. And what was that something else? Oh right. A territorial empire. As a result of the war, the U.S. got a bunch of new territories, notably the Philippines, Puerto Rico and Guam. We also used the war as an opportunity to annex Hawaii to protect our ships that would be steaming toward the Philippines. We didn’t annex Cuba, but we didn’t let it become completely independent, either. The Platt Amendment in the Cuban Constitution authorized American military intervention whenever it saw fit and gave us a permanent lease for a naval base at Guantanamo Bay. Thanks Thoughtbubble. So, Cuba and Puerto Rico were gateways to Latin American markets. Puerto Rico was particularly useful as a naval station. Hawaii, Guam, and especially the Philippines opened up access to China. American presence in China was bolstered by our contribution of about 3,000 troops to the multinational force that helped put down the Boxer Rebellion in 1900. But in the Philippines, where Americans had initially been welcome, opinion soon changed after it became clear that Americans were there to stay and exercise control. Emiliano Aguinaldo, leader of the Filipino rebellion against Spain, quickly turned against the U.S. because his real goal was independence and it appeared the U.S. would not provide it. The resulting Philippine War lasted 4 years, from 1899-1903. And 4,200 Americans were killed as well as over 100,000 Filipinos. The Americans committed atrocities, including putting Filipinos in concentration camps, torturing prisoners, rape, and executing civilians. And much of this was racially motivated and news of these atrocities helped to spur anti-imperialist sentiment at home, with Mark Twain being one of the most outspoken critics. Now, there was some investment in modernization in the Philippines, in railroads, schools, and public health, but the interests of the local people were usually subordinated to those of the wealthy. So, American imperialism in short looked like most other imperialism. So Constitution nerds will remember that the U.S. Constitution has no provision for colonies, only territory that will eventually be incorporated as states. Congress attempted to deal with this issue by passing the Foraker Act in 1900. This law declared that Puerto Rico would be an insular territory; its inhabitants would be citizens of Puerto Rico, not the United States and there would be no path to statehood. But this wasn’t terribly constitutional. Congress did extend U.S. citizenship to Puerto Ricans in 1917. Now it’s a commonwealth with its own government that has no voice in U.S. Congress or presidential elections and no control over its own defense or environmental policy. The Philippines were treated similarly to Puerto Rico, in a series of cases between 1901 and 1904 collectively called the Insular Cases. But Hawaii was treated differently. Because it had a sizeable population of American settlers who happened to be white. Ergo, it became a traditional territory with a path to statehood because white people and also pineapples. Now let’s briefly talk about anti-imperialism. There were lots of people who objected to imperialism on racial grounds, arguing that it might lead to, like, diversity. But there were also non-racist anti-imperialists who argued that empire itself with its political domination of conquered people was incompatible with democracy, which, to be fair, it is. The Democratic Party, which had supported intervention in Cuba, in 1900 opposed the Philippine War in its platform. Some Progressives opposed imperialism too because they believed that America should focus on its domestic problems. Yet those who supported imperialism were just as forceful. Among the most vocal was Indiana Senator Albert Beveridge who argued that imperialism was benevolent and would bring “a new day of freedom.” But, make no mistake, underneath it all, imperialism was all about trade. According to Beveridge, America’s commerce “must be with Asia. The Pacific is our ocean … Where shall we turn for consumers of our surplus? Geography answers the question. China is our natural customer.” In the end, imperialism was really driven by economic necessity. In 1902, Brooks Adams predicted in his book The New Empire that the U.S. would soon “outweigh any single empire, if not all empires combined.” Within 20 years America would be the world’s leading economic power. We didn’t have the most overseas territory, but ultimately that didn’t matter. Now, the reasons for imperialism, above all the quest for markets for American goods, would persist long after imperialism became recognized as antithetical to freedom and democracy. And we would continue to struggle to reconcile our imperialistic urges with our ideals about democracy until...now. Thanks for watching. I’ll see you next week. Crash Course is produced and directed by Stan Muller. Our script supervisor is Meredith Danko. The associate producer is Danica Johnson. The show is written by my high school history teacher, Raoul Meyer, Rosianna Rojas, and myself. And our graphics team is Thought Café. Every week there’s a new caption for the libertage. You can suggest captions in comments where you can also ask questions about today’s video that will be answered by our team of historians. Thanks for watching Crash Course and as we say in my hometown, don’t forget to be awesome. This is the part where Stan gets nervous, like, is he gonna go this way or this way or this way? I’m going this way. Imperialism -
Theories
Ibn Khaldun wrote that newly established dynasties, because they have social cohesion or Asabiyyah, are able to seek "expansion to the limit."[4]
The Soviet economist Nikolai Kondratiev theorized that capitalism advances in 50-year expansion/stagnation cycles, driven by technological innovation. The UK, Germany, the US, Japan and now China have been at the forefront of successive waves.
Crane Brinton in The Anatomy of Revolution saw the revolution as a driver of expansionism in, for example, Stalinist Russia, the United States and the Napoleonic Empire.
Christopher Booker believed that wishful thinking can generate a "dream phase" of expansionism such as in the European Union, which is short-lived and unreliable.
According to a 2023 study, important historical instances of territorial expansion have frequently happened because actors on the periphery of a state have acted without authorization from their superiors at the center of the state. Leaders subsequently find it difficult to withdraw from the newly captured areas due to "sunk costs, domestic political pressure, and national honor."[5]
Examples
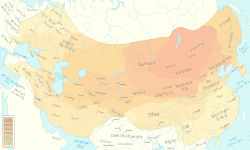
Every part of the world has experienced expansionism.[6][7] The religious imperialism and colonialism of Islam started with the early Muslim conquests, was followed by the religious Caliphate expansionisms, and ended with the Partition of the Ottoman Empire. In the 15th and 16th centuries, the Ottoman Empire entered a period of expansion. The Ottomans ended the Eastern Roman Empire with the conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed the Conqueror.[8]
The militarist and nationalistic reign of Russian Czar Nicholas I (1825–1855) led to wars of conquest against Persia (1826–1828) and Turkey (1828–1829). Various rebel tribes in the Caucasus region were crushed. A Polish revolt in 1830 was ruthlessly crushed. Russian troops in 1848 crossed into Austria-Hungary to put down the Hungarian Revolt. Russification policies were implemented to weaken minority ethnic groups. Pan-Slavist solidarity led to further war with Turkey (the sick man of Europe) in 1853 provoked Britain and France into invading Crimea.[9]
In Italy, Benito Mussolini sought to create a New Roman Empire, based around the Mediterranean. Italy invaded Ethiopia as early as 1935, Albania in early 1938, and later Greece. Spazio vitale ("living space") was the territorial expansionist concept of Italian Fascism. It was analogous to Nazi Germany's concept of Lebensraum and the United States' concept of "Manifest Destiny". Fascist ideologist Giuseppe Bottai likened this historic mission to the deeds of the ancient Romans.[10]
After 1937, Nazi Germany under Hitler laid claim to Sudetenland, unification (Anschluss) with Austria in 1938 and the occupation of the whole of the Czech lands the following year. After war broke out, Hitler and Stalin divided Poland between Germany and the Soviet Union. In a Drang nach Osten aimed at achieving Lebensraum for the German people, Germany invaded the Soviet Union in 1941.[11]

Expansionist nationalism is an aggressive and radical form of nationalism that incorporates autonomous patriotic sentiments with a belief in expansionism. The term was coined during the late 19th century as European powers indulged in the Scramble for Africa, but it has been most associated with militarist governments during the 20th century including Fascist Italy, Nazi Germany, the Japanese Empire, and the Balkans countries of Albania (Greater Albania), Bulgaria (Greater Bulgaria), Croatia (Greater Croatia), Hungary (Greater Hungary), Romania (Greater Romania) and Serbia (Greater Serbia).
In American politics after the War of 1812, Manifest Destiny was the ideological movement during America's expansion West. The movement incorporated expansionist nationalism with continentalism, with the Mexican War in 1846–1848 being attributed to it. Despite championing American settlers and traders as the people whom the government's military would be aiding, the Bent, St. Vrain and Company stated to be the most influential Indian trading company prior to the Mexican War, underwent a decline because of the and of traffic from American settlers by Beyreis. The company also lost the partner Charles Bent on January 19, 1847, to a riot caused by the Mexican War. Many in the Cheyennes, Comanches, Kiowas, and Pawnees tribes died from smallpox in 1839–1840, measles and whooping cough in 1845, and cholera in 1849, which had been brought by American settlers. The buffalo herds, sparse grasses, and rare waters were also depleted following the war as increased traffic by settlers moving to California during the Gold Rush.[12]
21st century
China
The People's Republic of China is accused of expansionism through its operations and claims in the South China Sea, which are concurrently claimed in part by Vietnam, the Philippines, Brunei, Malaysia and the Republic of China.[13]
Israel

Israel was established on May 14, 1948 following the end of World War II and the Holocaust. Its government has occupied the West Bank, the Gaza Strip, the Golan Heights, and the Sinai Peninsula since the Six-Day War, although the Sinai was later returned to Egypt in 1982[14][15][16] and Israel disengaged from the Gaza Strip in 2005. Israel also occupied southern Lebanon from February 1985 to May 2000.[17]
Iran
Iran, the largest Shi'ite state, has extended its influence across the entire Middle East, including Iraq, Lebanon, Syria, Yemen and Afghanistan by arming local militias.[18]
Russia

Russia under Vladimir Putin has had an aggressive posture since 2008, especially since 2014.[19] Events associated with Russia are the 2008 Russo-Georgian War and Russia's occupation of South Ossetia and Abkhazia; the Russo-Ukrainian War, which began in 2014 with the Annexation of Crimea and the war in Donbas and escalated into the ongoing full-scale Russian invasion of Ukraine in 2022; and the military intervention in Syria.
Turkey
Turkey's foreign policy is characterized, especially since 2010s by an aggressive expansionism, irredentism and interventionism in the Eastern Mediterranean and the neighboring Cyprus, Greece, Iraq, Syria, as well as in Africa, including Libya, and Nagorno-Karabakh.[a] Turkey has occupied foreign territories and stationed troops in them, following the 1974 Turkish invasion of Cyprus, the Turkish occupation of northern Syria since 2016 and the Turkish presence in northern Iraq since 2018.[26]
United States
The US has military bases in some sovereign countries it once occupied, including in Germany, Italy, Japan, Greenland, Iceland, Iraq, and formerly in Afghanistan. It continues to retain Guantanamo Bay Naval Base despite the protests of Cuba, and the US has military bases in various other countries with which it has allied.
Ideologies
In the 19th century, theories of racial unity evolved such as Pan-Germanism, Pan-Slavism, and Pan-Turkism and the related Turanism. In each case, the dominant nation (respectively, Prussia; the Russian Empire;[27] and the Ottoman Empire, especially under Enver Pasha) used those theories to legitimise their expansionist policies.
American ideology
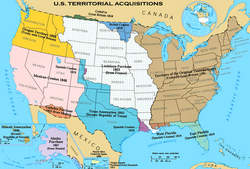
In terms of explaining the results of American expansion, this goes back to the 19th century when Frederick Jackson Turner produced his Frontier Thesis which made the case for the decisive role of American expansionism.[28][29] The free land enabled economic independence (as opposed to political dominance by landlords in Europe) and popular democracy in America.[30] The success of expansionism led to a deep belief in the superiority of the "American way of life," as shown by how it attracted tens of millions of immigrants. Economic success was supplemented by the confidence that Anglo Saxons were simply better at governing a nation.[31]
Further expansion far beyond the American continent, in the Philippines, at the turn of the century which was driven by a paternalistic United States as McKinley's objectives, he declared in mid-1899, were fourfold: "Peace first, then a government of law and order honestly administered, full security to life, property, and occupation under the Stars and Stripes."[32] However, the Philippines government was shared with the local political elite, which called for independence. In Washington Democrats rejected McKinley-style expansionism and in 1934 set the Philippines on the path to independence, which was achieved in 1946.[33]
It has also been posited that American leaders were pressured under traditional gender roles, which in turn made expansionism more likely. By the end of the 19th century President McKinley had been accustomed to being evaluated in terms of his manliness.[34] This also played in to the fact that in the late nineteenth century, men saw supporting the military as the ultimate test of being a man.[34] As a result, expansionism was a way of projecting manliness onto the electorate and in to society.
In popular culture
George Orwell's satirical novel Animal Farm is a fictional depiction, based on Stalin's Soviet Union, of a new elite seizing power, establishing new rules and hierarchies, and expanding economically while they compromise their ideals.
Robert Erskine Childers's novel The Riddle of the Sands portrays the threatening nature of the German Empire.
Elspeth Huxley's novel Red Strangers shows the effects on local culture of colonial expansion into Sub-Saharan Africa.
See also
- American imperialism
- British Empire
- French colonial empire
- Colonialism
- Early Muslim conquests
- Ethnic cleansing
- European colonization of the Americas
- Expansionist nationalism
- Greater Israel
- Irredentism
- List of irredentist claims or disputes
- Manifest Destiny
- Scramble for Africa, late 19th century
- Spread of Islam
References
- ^
An alternative definition sees "expansionism" as "a desire to annex additional territory" for reasons such as perceived needs for Lebensraum or resources, the intimidation of rivals, or the projection of an ideology.May, Ronald James, ed. (1979). The Indonesia-Papua New Guinea Border: Irianese Nationalism and Small State Diplomacy. Department of Political and Social Change, Research School of Pacific Studies, Australian National University. p. 43. ISBN 9780908160334. Retrieved 6 November 2020.
At this point, however, we must define 'expansionism' a little more precisely. I am interpreting it to mean a desire to annex additional territory either
[...]- for the sake of more lebensraum (living space) or resources (oil, copper, timber, etc.);
- for the sake of demonstrating the national power so as to intimidate neighbours;
- because of an ideology of national greatness, power
- ^ Knorr, Klaus (1952). Schumpeter, Joseph A.; Arendt, Hannah (eds.). "Theories of Imperialism". World Politics. 4 (3): 402–431. doi:10.2307/2009130. ISSN 0043-8871. JSTOR 2009130. S2CID 145320143.
- ^ "Manifest Destiny | History, Examples, & Significance". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 2019-05-07.
- ^ The Muqadimmah, 1377, pages 137-256
- ^ Anderson, Nicholas (2023). "Push and Pull on the Periphery: Inadvertent Expansion in World Politics". International Security. 47 (3): 136–173. doi:10.1162/isec_a_00454. S2CID 256390941.
- ^ See Abernethy (2009); Darwin (2008)
- ^ Wade, (2014).
- ^ Quataert, Donald (2005). The Ottoman Empire, 1700–1922 (2 ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 4. ISBN 978-0-521-83910-5.
- ^ Orlando Figes, Crimea (Penguin, 2011), chapter one
- ^ Rodogno, Davide (2006). Fascism's European Empire: Italian Occupation During the Second World War. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. pp. 46–47. ISBN 978-0-521-84515-1.
- ^ Sebastian Haffner, The Meaning of Hitler, Phoenix, 2000, chapters 2, 3 and 4
- ^ Beyreis, David (Summer 2018). "The Chaos of Conquest: The Bents and the Problem of American Expansion". Kansas History. 41 (2): 72–89 – via History Reference Center.
- ^ Simon Tisdall, 'Vietnam's fury at China's expansionism can be traced to a troubled history', The Guardian, 15/5/2004
- ^ "Carter Says Error Led U.S. to Vote Against Israelis". Washington Post. 4 March 1980. Retrieved 16 November 2021.
- ^ Masalha, Nur (2000). Imperial Israel and the Palestinians: politics of expansion. Sterling, VA: Pluto Press.
- ^ "Golan Heights Law". Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs. 14 December 1981. Retrieved 16 November 2021.
- ^ Norton, Augustus.R (2000). "Hizballah and the Israeli Withdrawal from Southern Lebanon". Journal of Palestine Studies. 30 (1): 22–35. doi:10.2307/2676479. JSTOR 2676479.
- ^ Arango, Tim (15 July 2017). "Iran Dominates in Iraq After U.S. 'Handed the Country Over'". New York Times. Retrieved 8 November 2019.
- ^ Walker, Peter (2015-02-20). "Russian expansionism may pose existential threat, says NATO general". The Guardian. Retrieved 2018-10-04.
- ^ Antonopoulos, Paul (2017-10-20). "Turkey's interests in the Syrian war: from neo-Ottomanism to counterinsurgency". Global Affairs. 3 (4–5): 405–419. doi:10.1080/23340460.2018.1455061. ISSN 2334-0460. S2CID 158613563.
- ^ Danforth, Nick (23 October 2016). "Turkey's New Maps Are Reclaiming the Ottoman Empire". Foreign Policy. Retrieved 2020-10-08.
- ^ "Turkey's Dangerous New Exports: Pan-Islamist, Neo-Ottoman Visions and Regional Instability". Middle East Institute. 21 April 2020. Retrieved 4 May 2021.
- ^ Sinem Cengiz (7 May 2021). "Turkey's militarized foreign policy provokes Iraq". Arab News. Retrieved 9 May 2021.
- ^ Asya Akca (8 April 2019). "Neo-Ottomanism: Turkey's foreign policy approach to Africa". Center for Strategic and International Studies. Retrieved 13 May 2021.
- ^ Slaviša Milačić (23 October 2020). "The revival of neo-Ottomanism in Turkey". World Geostrategic Sights. Retrieved 13 May 2021.
- ^ Yousif Ismael (18 May 2020). "Turkey's Growing Military Presence in the Kurdish Region of Iraq". Washington Institute. Retrieved 1 October 2022.
- ^ Orlando Figes, Crimea, Penguin, 2011, p.89
- ^ Richard Hofstadter, "Turner and the Frontier Myth". American Scholar 18#4 (1949), pp. 433–43. JSTOR 41206669.
- ^ LaFeber, Walter (1963). The New Empire: An Interpretation of American Expansion 1860 - 1898. United States of America: Cornell University Press. pp. 95–112. ISBN 0-8014-9048-0.
- ^ Stanley Elkins and Eric McKitrick, "A Meaning for Turner's Frontier: Part I: Democracy in the Old Northwest". Political Science Quarterly 69#3 (1954), pp. 321–53. doi:10.2307/2145274.
- ^ Burnett, Christina; Marshall, Burke (2001). Foreign in a Domestic Sense: Puerto Rico, American Expansion, and the Constitution. Durham: Duke University Press. p. 26. ISBN 1-283-06210-0.
- ^ LaFeber, Walter (2013-04-08). The New Cambridge History of American Foreign Relations (1 ed.). Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/cbo9781139015677. ISBN 978-1-139-01567-7.
- ^ Dean Kotlowski, "Independence or Not? Paul V. McNutt, Manuel L. Quezon, and the Re-examination of Philippine Independence, 1937–9" International History Review 32#3 (2010), pp. 501–531 online
- ^ a b Hoganson, Kristin (1998). Fighting for American Manhood. New Haven and London: Yale University Press. p. 95. ISBN 978-0-300-08554-9.
Further reading
- Abernethy, David B. The dynamics of global dominance: European overseas empires, 1415-1980 (Yale University Press, 2000).
- Darwin, John. After Tamerlane: the global history of empire since 1405 ( Bloomsbury, 2008).
- Edwards, Zophia, and Julian Go. "The Forces of Imperialism: Internalist and Global Explanations of the Anglo-European Empires, 1750–1960". Sociological Quarterly 60.4 (2019): 628–653.
- MacKenzie, John M. "Empires in world history: characteristics, concepts, and consequences". in The Encyclopedia of Empire (2016): 1-25.
- Wade, Geoff, ed. Asian Expansions: The Historical Experiences of Polity Expansion in Asia (Routledge, 2014).
- Wesseling, Hendrik. The European Colonial Empires: 1815-1919 (Routledge, 2015).
