Duchy of Jawor | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1274–1392 | |||||||||
 Silesia in 1274: Jawor Duchy in red | |||||||||
| Status | Silesian duchy | ||||||||
| Capital | Jawor | ||||||||
| Historical era | Middle Ages | ||||||||
• Partitioned from Legnica | 1274 | ||||||||
| 1291 | |||||||||
• Reunited with Świdnica | 1346 | ||||||||
• Annexed by Bohemia | 1392 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Duchy of Jawor (Polish: Księstwo Jaworskie, German: Herzogtum Jauer) was one of the Duchies of Silesia established in 1274 as a subdivision of the Duchy of Legnica. It was ruled by the Silesian Piasts, with its capital at Jawor in Lower Silesia.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:95361124 384
-
Legend of Chojnik Castle
-
Western Poland (#02): Castle Chojnik
-
ZAMEK W NIEDZICY | NIEDZICA CASTLE
Transcription
Geography

The original Duchy stretched from Jawor on the Nysa Szalona River westwards along the northern slopes of the Western Sudetes to the Jizera Mountains and the Kwisa River, which formed the Silesian border with the former Milceni lands of Upper Lusatia. In the north it bordered the remaining Duchy of Legnica and in the east the Duchy of Silesia-Wrocław.
It included the towns of Bolków, Kamienna Góra, Lubawka, Lwówek, Świerzawa and (from 1277) Strzegom.
History
The Silesian Duchy of Legnica since 1248 had been under the rule of Duke Bolesław II Rogatka. When Bolesław's eldest son Henry V the Fat succeeded his father as Duke of Legnica in 1278, he gave the Jawor subdivision to his younger brothers Bolko I the Strict and Bernard the Lightsome. In 1281 Bernard was made a Duke of Lwówek in the western part of the Jawor lands.

In 1286 Bolko I again inherited Lwówek from his brother and in 1291 further enlarged his territories by receiving Świdnica and Ziębice from his elder brother Henry V of Legnica. These territories had formed the southern part of the Duchy of Silesia-Wrocław, which Henry V had acquired upon the death of his cousin Duke Henry IV Probus the year before. Henry V, though backed by King Wenceslaus II of Bohemia, was in need for support to retain his Wrocław acquisitions against the claims of rivalling Duke Henry III of Głogów. From 1288 Bolko I had a new residence erected at Książ Castle in the Świdnica lands. For a brief period, his duchy is sometimes known as the Duchy of Jawor-Świdnica.
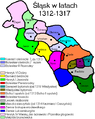
Bolko's attempts to gain the Duchy of Nysa failed, nevertheless he occupied Paczków and acquired Chojnów from Duke Henry III of Głogów. After his death in 1301, his sons finally divided their territories in 1312: the lands around Świdnica and Ziębice were again split off into separate duchies, while Jawor was ruled by Duke Henry I. After his death in 1346, the duchy was reunited with Świdnica under the rule of his nephew Bolko II the Small.
Bolko II was the last Piast duke to retain his independence from the Kingdom of Bohemia, however as he had no male heirs he signed an inheritance treaty with King Charles IV of Luxembourg, who married Bolko's niece Anna von Schweidnitz in 1353. The duke died in 1368 and after the death of his widow Agnes of Habsburg in 1392 his duchy was finally annexed by the Bohemian Crown.
Gallery
-
Growth of the Jawor Duchy (in red) in the late 1290s
-
Jawor Duchy (in light green) is reduced to its original size in 1312.
See also
Literature
- Historische Kommission für Schlesien (Hrsg.): Geschichte Schlesiens, Bd. 1. Sigmaringen 1988, ISBN 3-7995-6341-5, p. 146, 150, 172f., 185f., 211, 221f. and 289.
- Hugo Weczerka: Handbuch der historischen Stätten: Schlesien. Stuttgart, 1977, ISBN 3-520-31601-3, p. 206–210 and 491–496, genealogy on p. 593.
- Joachim Bahlcke: Schlesien und die Schlesier, Langen-Müller-Verlag, 2000, ISBN 3-7844-2781-2
- Žáček, Rudolf (2004). Dějiny Slezska v datech [History of Silesia in Dates] (in Czech). Prague: Libri. pp. 420, 446–448. ISBN 80-7277-172-8.
51°03′00″N 16°12′00″E / 51.050000°N 16.200000°E