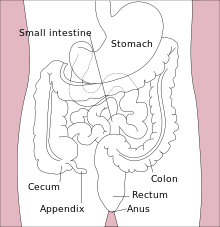
Distal intestinal obstruction syndrome (DIOS) involves obstruction of the distal part of the small intestines by thickened intestinal content and occurs in about 20% of mainly adult individuals with cystic fibrosis.[1] DIOS was previously known as meconium ileus equivalent, a name which highlights its similarity to the intestinal obstruction seen in newborn infants with cystic fibrosis.[2] DIOS tends to occur in older individuals with pancreatic insufficiency. Individuals with DIOS may be predisposed to bowel obstruction, though it is a separate entity than true constipation.[2]
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:862 10763 91534 869
-
Bowel Obstruction - Causes and Pathophysiology
-
Bowel Obstruction and Ileus: Large Bowel Obstruction & Ogilvie Syndrome – Radiology | Lecturio
-
Small Bowel Obstruction (SBO) | Risk Factors, Causes, Signs & Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment
Transcription
Signs and symptoms
Signs and symptoms of DIOS include a sudden onset of crampy abdominal pain, vomiting, and a palpable mass (often in the right lower quadrant) in the abdomen. The characteristic abdominal pain is typically located in the center or right lower quadrant of the abdomen.[1] X-rays of the abdomen may reveal stool in the colon and air-fluid levels in the small intestines.[citation needed]
Diagnosis
A complete history and physical examination can be suggestive, especially if a palpable mass in the right lower quadrant of the abdomen is present (though this can be present in the absence of DIOS). Ultrasound and computed tomography (CT) imaging of the abdomen can confirm the diagnosis by demonstrating dilated loops of intestine with material in the intestinal lumen with bubbles.[1] Air-fluid levels may be seen in those affected by DIOS.[1]
Classification
DIOS is sometimes classified by the degree of obstruction as incomplete or complete DIOS.[3]
Differential diagnosis
Additional diagnoses which may present with similar symptoms to DIOS include severe constipation, appendicitis, and intussusception.[1]
Management
Differentiation of DIOS from constipation is generally performed by unit specializing in the treatment of cystic fibrosis. Adequate hydration and an aggressive regimen of laxatives are essential for treatment and prevention of DIOS. Osmotic laxatives such as polyethylene glycol are preferred.[1] Individuals prone to DIOS tend to be at risk for repeated episodes and often require maintenance therapy with pancreatic enzyme replacement, hydration and laxatives (if the symptoms are also mild).[4][5] Oral contrast instillation into the colon/ileum under radiological control has been found to reduce the need for surgical intervention.[citation needed]
References
- ^ a b c d e f Kelly, T; Buxbaum, J (July 2015). "Gastrointestinal Manifestations of Cystic Fibrosis". Digestive Diseases and Sciences (Review). 60 (7): 1903–13. doi:10.1007/s10620-015-3546-7. PMID 25648641. S2CID 25453958.
- ^ a b Stringer, David A.; Babyn, Paul S. (2000). Pediatric Gastrointestinal Imaging and Intervention. PMPH-USA. p. 347. ISBN 9781550090796.
- ^ Feldman, Mark; Friedman, Lawrence S.; Brandt, Lawrence J. (2010). Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease E-Book: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, Management, Expert Consult Premium Edition - Enhanced Online Features. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 945. ISBN 978-1437727678.
- ^ Ludwig, Stephen (2008). Visual Handbook of Pediatrics and Child Health: The Core. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 283. ISBN 9780781795050.
- ^ Mighten, Janice (2012). Children's Respiratory Nursing. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 9781118278277.
External links
- http://www.cfmedicine.com/htmldocs/CFText/dios.htm Archived 2015-06-29 at the Wayback Machine
- http://www.rbht.nhs.uk/healthprofessionals/clinical-departments/cystic-fibrosis/clinical-guidelines/nutritional-and-gastrointestinal-care/constipation-and-distal-intestinal-obstructive-syndrome/ Archived 2016-04-20 at the Wayback Machine