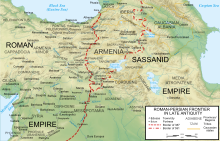
Bezabde or Bazabde was a fortress city on the eastern Roman frontier. Located in Zabdicene, it played a role in the Roman-Persian Wars of the 4th century.[1][2] It was besieged two times in 360, narrated in detail by Ammianus Marcellinus.[1] The Sasanians led by Shapur II captured Bezabde, despite adamant resistance from three Roman legions and local archers.[1] The Roman counterattack led by Constantius II failed, but it returned in Roman hands after the Sasanians withdrew.[1] Bezabde was ceded to the Sasanians by the Perso-Roman Peace Treaty of 363, after which it disappeared from historical records.[1]
James Crow notes: "It was formerly thought that Bezabde stood close to modern Cizre, on the west bank of the Tigris. However archaeological survey has located a major Late Roman site at Eski Hendek, 13 km (8 miles) north-west of Cizre. The outline of the city is trapezoidal and was aligned above the river. It may be seen to be divided into two distinct enclosures, with an annexe to the west and clear traces of projecting towers and multiple defences".[1]
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/1Views:599
-
Ain Diwar, Roman bridge in Rojava, Syria
Transcription
References
- ^ a b c d e f Crow 2018a, p. 235.
- ^ Crow 2018b, p. 1605.
Sources
- Crow, James (2018a). "Bezabde". In Nicholson, Oliver (ed.). The Oxford Dictionary of Late Antiquity. Oxford University Press.
- Crow, James (2018b). "Zabdicene". In Nicholson, Oliver (ed.). The Oxford Dictionary of Late Antiquity. Oxford University Press.
37°24′08″N 42°04′00″E / 37.40222°N 42.06667°E
