| Bdeogale | |
|---|---|

| |
| Drawing, 1850 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Suborder: | Feliformia |
| Family: | Herpestidae |
| Subfamily: | Herpestinae |
| Genus: | Bdeogale Peters, 1850 |
| Type species | |
| Bdeogale crassicauda Peters, 1850
| |
| Species | |
|
see text | |

| |
| Bdeogale crassicauda - blue Bdeogale jacksoni - violet Bdeogale nigripes - green | |
Bdeogale is a mongoose genus that was proposed by Wilhelm Peters in 1850 based on a mongoose specimen collected in Mozambique.[1] Bdeogale species have compact paws with four symmetrical toes, round ears and a blunt muzzle with a broad round and bare rhinarium. The genus contains four species that are primarily terrestrial and omnivorous and forage in dense vegetation.[2]
Species
| Name | Distribution and IUCN Red List status |
|---|---|
| Bushy-tailed mongoose (B. crassicauda) Peters, 1852[3] |
Kenya and Tanzania LC[4] |
| Black-footed mongoose (B. nigripes) Pucheran, 1855[5] | 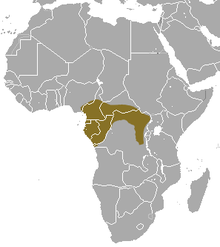 LC[6] |
| Jackson's mongoose (B. jacksoni) (Thomas, 1894)[7] |  NT[8] |
| Sokoke dog mongoose (B. omnivora) Heller, 1914[9] | Kenya and Tanzania VU[10] |
References
- ^ Peters, W. (1850). "Bdeogale". Sitzungsberichte der Gesellschaft Naturforschender Freunde zu Berlin: 94.
- ^ Kingdon, J. (2015). "Bdeogale". The Kingdon Field Guide to African Mammals (Second ed.). London, New Delhi, New York, Sydney: Bloomsbury Publishing. p. 441. ISBN 9781472925312.
- ^ Peters, W. (1852). "Mittheilung über die in Mossambique beobachteten Mangusten". Verhandlungen der Königlich Preussischen Akademie der Wissenschaften zu Berlin: 81–82.
- ^ White, P.A.; Fischer, C.; Hausser, Y.; Foley, C. & Do Linh San, E. (2016). "Bdeogale crassicauda". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41591A97163568.
- ^ Pucheran, J.P. (1855). "Les Mammifères de la côte occidental d'Afrique". Revue et magasin de zoologie pure et appliquée. 2. 7: 111.
- ^ Angelici, F. M. & Do Linh San, E. (2015). "Bdeogale nigripes". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T41592A45205243.
- ^ Thomas, O. (1894). "On a new African Genus of Mustelidae". The Annals and Magazine of Natural History; Zoology, Botany, and Geology. 6. 13 (78): 522–524.
- ^ De Luca, W.; Rovero, F. & Do Linh San, E. (2015). "Bdeogale jacksoni". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T2675A45196818.
- ^ Heller, E. (1914). "New antelopes and carnivores from British East Africa". Smithsonian Miscellaneous Collections. 61 (2240): 1–15.
- ^ Foley, C. & Do Linh San, E. (2016). "Bdeogale omnivora". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T136686A45221619.
External links


