An associative entity is a term used in relational and entity–relationship theory. A relational database requires the implementation of a base relation (or base table) to resolve many-to-many relationships. A base relation representing this kind of entity is called, informally, an associative table.

As mentioned above, associative entities are implemented in a database structure using associative tables, which are tables that can contain references to columns from the same or different database tables within the same database.
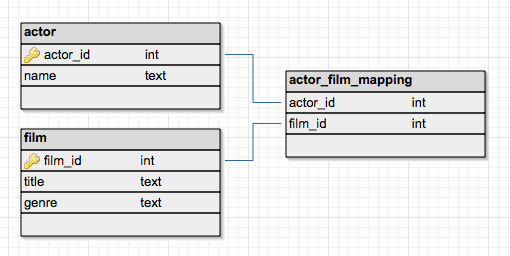
An associative (or junction) table maps two or more tables together by referencing the primary keys (PK) of each data table. In effect, it contains a number of foreign keys (FK), each in a many-to-one relationship from the junction table to the individual data tables. The PK of the associative table is typically composed of the FK columns themselves.
Associative tables are colloquially known under many names, including association table, bridge table, cross-reference table, crosswalk, intermediary table, intersection table, join table, junction table, link table, linking table, many-to-many resolver, map table, mapping table, pairing table, pivot table (as used incorrectly in Laravel—not to be confused with the correct use of pivot table in spreadsheets), or transition table.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:2 4194 3223 390
-
Associative Entity||Examples of Associative Entity|| ER diagram 2021
-
Associative Entity with example and explain strong entity and weak entity in Hindi/Urdu
-
Associative entities
Transcription
Using associative tables
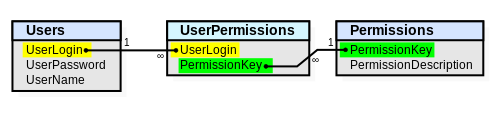
An example of the practical use of an associative table would be to assign permissions to users. There can be multiple users, and each user can be assigned zero or more permissions. Individual permissions may be granted to one or more users.
CREATE TABLE Users (
UserLogin varchar(50) PRIMARY KEY,
UserPassword varchar(50) NOT NULL,
UserName varchar(50) NOT NULL
);
CREATE TABLE Permissions (
PermissionKey varchar(50) PRIMARY KEY,
PermissionDescription varchar(500) NOT NULL
);
-- This is the junction table.
CREATE TABLE UserPermissions (
UserLogin varchar(50) REFERENCES Users (UserLogin),
PermissionKey varchar(50) REFERENCES Permissions (PermissionKey),
PRIMARY KEY (UserLogin, PermissionKey)
);
A SELECT-statement on a junction table usually involves joining the main table with the junction table:
SELECT * FROM Users
JOIN UserPermissions USING (UserLogin);
This will return a list of all users and their permissions.
Inserting into a junction table involves multiple steps: first inserting into the main table(s), then updating the junction table.
-- Creating a new User
INSERT INTO Users (UserLogin, UserPassword, UserName)
VALUES ('SomeUser', 'SecretPassword', 'UserName');
-- Creating a new Permission
INSERT INTO Permissions (PermissionKey, PermissionDescription)
VALUES ('TheKey', 'A key used for several permissions');
-- Finally, updating the junction
INSERT INTO UserPermissions (UserLogin, PermissionKey)
VALUES ('SomeUser', 'TheKey');
Using foreign keys, the database will automatically dereference the values of the UserPermissions table to their own tables.
See also
References
- Hoffer, Jeffrey A.; Prescott, Mary B.; McFadden, Fred R. (2004). Modern Database Management (7th ed.). Prentice Hall. ISBN 978-0131453203.
- Codd, E. F. (1970). "A Relational Model of Data for Large Shared Data Banks". Communications of the ACM. 13 (6). ACM: 377–387. doi:10.1145/362384.362685.
