| Asphyxiating thoracic dysplasia | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Jeune syndrome, asphyxiating thoracic chondrodystrophy, infantile thoracic dystrophy |
 | |
| CXR of a newborn with asphyxiating thoracic dysplasia. Note the short ribs. | |
| Specialty | Medical genetics |
| Symptoms | Narrow chest, short ribs, shortened bones of the arms and legs, unusually shaped pelvis, and extra fingers and/or toes |
| Treatment | Mechanical ventilation, endotracheal suctioning, postural drainage, Vertical expandable prosthetic titanium rib (VEPTR), Lateral thoracic expansion, or other chest reconstruction surgeries. |
| Frequency | 1 in 100,000 to 130,000 |
| Deaths | Mortality of affected: 60-70% |
Asphyxiating thoracic dysplasia (ATD), also known as Jeune syndrome, is a rare inherited bone growth disorder (autosomal recessive skeletal dysplasia) [1] that primarily affects the thoracic region. It was first described in 1955 by the French pediatrician Mathis Jeune.[2] Common signs and symptoms can include a narrow chest, short ribs, shortened bones in the arms and legs, short stature, and extra fingers and toes (polydactyly). The restricted growth and expansion of the lungs caused by this disorder results in life-threatening breathing difficulties; occurring in 1 in every 100,000-130,000 live births in the United States.[1][3]
People who are affected with this disorder live short lives either only into infancy or early childhood.[2] If they live beyond childhood, breathing problems can improve with age, but there is a possibility of developing severe kidney or heart problems. Several mutations in different genes such as IFT80, DYNC2H1, WDR19, IFT140 and TTC21B have been identified in some families with the condition as possible causes of the disorder. Treatment is based on the signs and symptoms present in each person.[4]
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/5Views:7 8644632 5944661 166
-
Jeune Syndrome
-
Congenital thoracic wall deformity
-
Imaging of skeletal Dysplasia - Prof. Dr. Hassan Elkiki
-
Skeletal Dysplasia
-
Pediatric Film reading session (II) - Prof. Dr. Hassan El-Kiki
Transcription
Jeune Syndrome is one of the rarest syndrome rare syndromes are unique because they pose a challenge to healthcare providers at level of diagnosis at level of counselling and ultimately when it comes to management lets start with our discussion 2 day old male baby weighing 2.7 kilos presented with complaint of difficulty in breathing since 2 hours baby was preterm appropriate for gestational age with history of delayed cry at the time of presentation saturation was 88% to 90% and heart rate 124 beats per minute on respiratory system examination nasal flaring was present chest was bell shaped tachypnea and intercostal retractions were noted on examination chest of this baby is bell shaped as a result nipples seem to lie more laterally there are five fingers in both hand and feet if you observe carefully you will note that both upper and lower extremities are short on further evaluation chest x-ray of this baby shows bell shaped rib cage short flaring ribs and high riding clavicles also known as handle-bar clavicles x-ray pelvis and lower limb shows short iliac bones and trident acetabulum trident acetabulum is an acetabulum having three inferior pointing spikes resembling upside down trident trident is also known as '' Trishul '' of Lord Shiva of Hindu Mythology besides Jeune Syndrome trident acetabulum is also seen in Ellis van creveld syndrome and Thanatophoric Dysplasia Jeune Syndrome is is an autosomal recessive disorder with multisystem involvement variable degree of pulmonary hypoplasia is the result of short rib thoracic dysplasia and is the key pathology in this syndrome besides skeletal abnormalities variable involvement of brain eye,heart,kidneys liver,pancreas,intestines and genitalia may be present and should be looked for at birth these babies may have difficulty initiating breath as evident in our case by history of delayed cry healthcare providers must be aware of this fact and must be ready for carrying out resuscitation at birth after birth these babies may not need,may need minimum or or may need more respiratory support either continuously or intermittently degree of respiratory support needed is directly proportional to degree of pulmonary hypoplasia and is a good bedside marker for assessment another approach in the management is VEPTR which is Vertical Expandable Prosthetic Titanium Rib VEPTR is a curved metal device with hooks at both ends surgically attached to patient's ribs,spine or pelvis this device can be adjusted to create sufficient and and more physiologically simulating rib cage for lungs to expand and grow more normally Jeune syndrome is one of the diseases where there exists no definitive management supportive respiratory support and evolution of VEPTR over years is the result of rationale thinking of of heathcare professionals evolved over years enthusiasm and perseverance of healthcare professionals involved make the real difference in managing these cases
Types
| Type | OMIM | Gene | Locus |
|---|---|---|---|
| ATD1 | 208500 | ? | 15q13 |
| ATD2 | 611263 | IFT80 | 3q |
| ATD3 | 613091 | DYNC2H1 | 11q |
Signs and symptoms
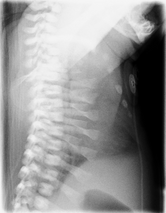
Jeune syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that affects the way a child's cartilage and bones develop. It begins before the child is born and primarily affects the child's rib cage, pelvis, arms and legs.[5] Usually, problems with the rib cage cause the most serious health problems for children with Jeune syndrome. Their rib cages (thorax) are smaller and narrower than usual, which inhibits the child's lungs from developing fully or expanding when they inhale. The child may breathe rapidly and shallowly. They may have trouble breathing when they have an upper or lower respiratory infection, like pneumonia. Breathing trouble can range from mild to severe. In some children, it is not noticeable, aside from fast breathing; however, in others, breathing problems can be fatal. About 60% to 70% of children with this condition die from respiratory failure as babies or young children. Children with Jeune syndrome who survive often develop problems with their kidneys, and over time they may experience kidney failure.[2] As a result, few children with Jeune syndrome live into their teen years. Children with Jeune syndrome have a form of dwarfism. They are short in stature, and their arms and legs are shorter than most people's.[6]
Diagnosis
Jeune syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive ciliopathy.[7] This diagnosis is grouped with other chest problems called thoracic insufficiency syndrome (TIS). Diagnosis of Jeune syndrome can be made as early as before birth if signs and symptoms are apparent on an ultrasound; however, diagnosis after birth usually occurs through X-rays and genetic testing, such as the tests found on the Genetic Testing Registry (GTR).[8]
Treatment
Medical care
In order to help relieve respiratory distress, mechanical ventilation is required in most severe cases; while pulmonary infections that tend to lead to respiratory failure occur in less severe cases. In order to treat these infections, doctors may suggest antibiotics, endotracheal suctioning, or postural drainage.[9]
Surgical care
In severe cases, surgical action is needed; otherwise, failure to intervene can result in pulmonary damage and eventual fatality. Vertical expandable prosthetic titanium rib (VEPTR) surgery is the most common treatment for severe chest wall deformities. During this procedure, one or more titanium rods are attached to the ribs near the spine, which allow space for the patient's lungs to develop. Small adjustments are made every four to six months through a small incision in the patient's back.[10] Alternatively, lateral thoracic expansion is used to enlarge the chest wall by separating the ribs from their periosteum and covering them with titanium struts. This procedure is common among patients older than a year due to its safe and effective outcome. Chest reconstruction is another surgical procedure that promotes thoracic cage growth. It can be done as an enlargement of the thoracic cage by sternotomy and fixation with bone grafts, or a methylmethacrylate prostheses plate.[7]
References
- ^ a b Kondo, Hiroaki; Hyuga, Shunsuke; Fujita, Tomoe; Adachi, Mariko; Mochizuki, Junko; Okutomi, Toshiyuki (2021-02-11). "First Report of Spinal Anesthesia for Cesarean Delivery in a Parturient With Jeune Syndrome: A Case Report". A&A Practice. 15 (2): e01400. doi:10.1213/XAA.0000000000001400. ISSN 2575-3126. PMID 33577174. S2CID 231898002.
- ^ a b c de Vries J, Yntema JL, van Die CE, Crama N, Cornelissen EA, Hamel BC (January 2010). "Jeune syndrome: description of 13 cases and a proposal for follow-up protocol". European Journal of Pediatrics. 169 (1): 77–88. doi:10.1007/s00431-009-0991-3. PMC 2776156. PMID 19430947.
- ^ Saletti D, Grigio TR, Tonelli D, Ribeiro Júnior OD, Marini F. Case report: anesthesia in patients with asphyxiating thoracic dys-trophy: Jeune syndrome. Rev Bras Anestesiol. 2012;62:424–431.
- ^ "Jeune syndrome | Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD) – an NCATS Program". rarediseases.info.nih.gov. Retrieved 2019-11-14.
- ^ Reference, Genetics Home. "Asphyxiating thoracic dystrophy". Genetics Home Reference. Retrieved 2019-11-14.
- ^ Jeune M, Beraud C, Carron R (1955). "[Asphyxiating thoracic dystrophy with familial characteristics]". Archives Françaises de Pédiatrie (in French). 12 (8): 886–91. ISSN 0003-9764. PMID 13292988.
- ^ a b "Asphyxiating Thoracic Dystrophy (Jeune Syndrome) Treatment & Management: Approach Considerations, Medical Care, Surgical Care". WebMD. 2019-11-10.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Bianchi, Diana W.; Crombleholme, Timothy M.; D'Alton, Mary E. (2000). Fetology: Diagnosis & Management of the Fetal Patient. McGraw Hill Professional. ISBN 9780838525708.
- ^ Mayer, Oscar Henry (June 2009). "Management of thoracic insufficiency syndrome". Current Opinion in Pediatrics. 21 (3): 333–343. doi:10.1097/mop.0b013e328329a500. ISSN 1040-8703.
- ^ Philadelphia, The Children's Hospital of (2018-07-31). "Jeune Syndrome". www.chop.edu. Retrieved 2019-11-14.
