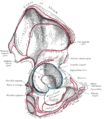
| Anterior superior iliac spine | |
|---|---|
 The obturator membrane (anterior superior iliac spine visible in upper right of illustration) | |
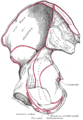
 Anterior superior iliac spine labeled second to bottom, right | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | spina iliaca anterior superior |
| TA98 | A02.5.01.111 |
| TA2 | 1327 |
| FMA | 49465 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
The anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS) is a bony projection of the iliac bone, and an important landmark of surface anatomy. It refers to the anterior extremity of the iliac crest of the pelvis. It provides attachment for the inguinal ligament, and the sartorius muscle.[1] The tensor fasciae latae muscle attaches to the lateral aspect of the superior anterior iliac spine, and also about 5 cm away at the iliac tubercle.[2][3]
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/5Views:25 3988 2591 39518 351194 792
-
Ilium: Body & Bony Landmarks – Anatomy | Lecturio
-
Anterior superior iliac spine
-
Anterior superior iliac spine avulsion
-
Surface Anatomy: Pelvis, Anterior Landmarks on Model
-
Pelvis Hip Bones Anatomy (Os Coxae, Pelvic Girdle) - Ilium, Ischium, Pubis
Transcription
Structure
The anterior superior iliac spine refers to the anterior extremity of the iliac crest of the pelvis. This is a key surface landmark, and easily palpated. It provides attachment for the inguinal ligament, the sartorius muscle,[1][4] and the tensor fasciae latae muscle.[2][3]
A variety of structures lie close to the anterior superior iliac spine, including the subcostal nerve,[5] the femoral artery (which passes between it and the pubic symphysis),[4] and the iliohypogastric nerve.[6]
Clinical significance
The anterior superior iliac spine provides a clue in identifying some other clinical landmarks, including McBurney's point, Roser-Nélaton line, and true leg length. It is an important surface landmark for various surgical approaches, such as treatment of hernia.[7] The severity of symptoms of damage to the iliohypogastric nerve can show whether damage occurred above or below the anterior superior iliac spine.[6]
Bone may be harvested from the nearby iliac crest for use elsewhere in the body.[5] As the subcostal nerve lies close to the anterior superior iliac spine, this is put at risk of damage.[5]
The iliotibial tract may be irritated where it passes over the anterior superior iliac spine in iliotibial band syndrome.[3]
The line around anterior superior iliac spine is sometimes called the panty line or "bikini line".[8] It is considered to be a "discreet" location for concealing cosmetic surgery scars and ports.[9]
Additional images
-
Right hip bone. External surface.
-
Right hip bone. Internal surface.
-
The subcutaneous inguinal ring
-
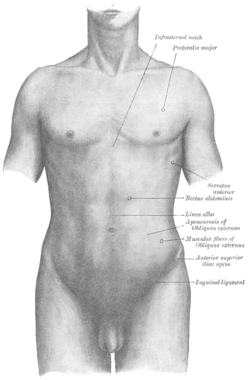
ASIS visible at top left, as the origin of several muscles
-
Location of McBurney's point (1), which is located two thirds the distance from the umbilicus (2) to the anterior superior iliac spine (3)
See also
References
- ^ a b Chaitow, Leon; DeLany, Judith (2011-01-01), Chaitow, Leon; DeLany, Judith (eds.), "Chapter 12 - The hip", Clinical Application of Neuromuscular Techniques, Volume 2 (Second Edition), Oxford: Churchill Livingstone, pp. 391–445, doi:10.1016/b978-0-443-06815-7.00012-7, ISBN 978-0-443-06815-7, retrieved 2020-12-15
- ^ a b Garten, Hans (2013), "M. tensor fasciae latae", The Muscle Test Handbook, Elsevier, pp. 236–237, doi:10.1016/b978-0-7020-3739-9.00091-2, ISBN 978-0-7020-3739-9, retrieved 2020-12-15
- ^ a b c Chaitow, Leon; DeLany, Judith (2011-01-01), Chaitow, Leon; DeLany, Judith (eds.), "Chapter 11 - The pelvis", Clinical Application of Neuromuscular Techniques, Volume 2 (Second Edition), Oxford: Churchill Livingstone, pp. 299–389, doi:10.1016/b978-0-443-06815-7.00011-5, ISBN 978-0-443-06815-7, retrieved 2020-12-15
- ^ a b Jacob, S. (2008-01-01), Jacob, S. (ed.), "Chapter 6 - Lower limb", Human Anatomy, Churchill Livingstone, pp. 135–179, doi:10.1016/b978-0-443-10373-5.50009-9, ISBN 978-0-443-10373-5, retrieved 2020-12-15
- ^ a b c Rea, Paul (2015-01-01), Rea, Paul (ed.), "Chapter 3 - Lower Limb Nerve Supply", Essential Clinically Applied Anatomy of the Peripheral Nervous System in the Limbs, Academic Press, pp. 101–177, doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-803062-2.00003-6, ISBN 978-0-12-803062-2, retrieved 2020-12-15
- ^ a b Mirjalili, S. Ali (2015-01-01), Tubbs, R. Shane; Rizk, Elias; Shoja, Mohammadali M.; Loukas, Marios (eds.), "Chapter 45 - Anatomy of the Lumbar Plexus", Nerves and Nerve Injuries, San Diego: Academic Press, pp. 609–617, doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-410390-0.00047-0, ISBN 978-0-12-410390-0, retrieved 2020-12-15
- ^ Molloy, Robert E. (2005-01-01), Benzon, Honorio T.; Raja, Srinivasa N.; Molloy, Robert E.; Liu, Spencer S. (eds.), "Chapter 75 - Truncal Blocks: Intercostal, Paravertebral, Interpleural, Suprascapular, Ilioinguinal, and Iliohypogastric Nerve Blocks", Essentials of Pain Medicine and Regional Anesthesia (Second Edition), Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone, pp. 636–644, doi:10.1016/b978-0-443-06651-1.50079-4, ISBN 978-0-443-06651-1, retrieved 2020-12-15
- ^ Kim, Ji Hun (2013). "Robotic cholecystectomy with new port sites". World Journal of Gastroenterology. 19 (20): 3077. doi:10.3748/wjg.v19.i20.3077. ISSN 1007-9327. PMC 3662947. PMID 23716987.
- ^ Leggett, P.L.; Bissell, C.D.; Churchman-Winn, R. (2001). "Cosmetic minilaparoscopic cholecystectomy". Surgical Endoscopy. 15 (10): 1229–1231. doi:10.1007/s004640041018. ISSN 0930-2794.
External links
- "Anatomy diagram: 03281.000-3". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2012-07-22.
- Diagram at Wayne State