In organic chemistry, alkanolamines (amino alcohols) are organic compounds that contain both hydroxyl (−OH) and amino (−NH2, −NHR, and −NR2) functional groups on an alkane backbone. Most alkanolamines are colorless.[1]
- Alkanolamines
-
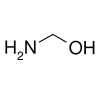
Methanolamine, from the reaction of ammonia with formaldehyde
-
-
2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol is a precursor to oxazolines
-
-
Sphingosine is a component of some cell membrane.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:1 41296017 681
-
THE CHEMiCAL PROPERTiES OF AMiNES
-
QFLO - Drag Reducing Agent Chemical Supplier and Application Specialists
-
Organic Chemistry 51B. Lecture 24. Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution.
Transcription
1-Aminoalcohols
1-Aminoalcohols are better known as hemiaminals. Methanolamine is the simplest member.
2-Aminoalcohols
2-Aminoalcohols are an important class of organic compounds that are often generated by the reaction of amines with epoxides:
- C2H4O + R−NH2 → RNHC2H4OH
Simple alkanolamines are used as solvents, synthetic intermediates, and high-boiling bases.[2]
Hydrogenation or hydride reduction of amino acids gives the corresponding 2-aminoalcohols. Examples include prolinol (from proline), valinol (from valine), tyrosinol (from tyrosine).
Key members: ethanolamine, dimethylethanolamine, N-methylethanolamine, Aminomethyl propanol. Two popular drugs, often called alkanolamine beta blockers, are members of this structural class: propranolol, pindolol. Isoetarine is yet another medicinally useful derivative of ethanolamine.[citation needed]
1,3-, 1,4-, and 1,5-amino alcohols
- Heptaminol, a cardiac stimulant
- Propanolamines
Natural products
Most proteins and peptides contain both alcohols and amino groups. Two amino acids are alkanolamines, formally speaking: serine and hydroxyproline.
- Veratridine and veratrine
- Tropane alkaloids such as atropine
- hormones and neurotransmitters epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline)
References
- ^ Smith, Michael B.; March, Jerry (2007), Advanced Organic Chemistry: Reactions, Mechanisms, and Structure (6th ed.), New York: Wiley-Interscience, ISBN 978-0-471-72091-1
- ^ Martin Ernst; Johann-Peter Melder; Franz Ingo Berger; Christian Koch (2022). "Ethanolamines and Propanolamines". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a10_001.pub2. ISBN 978-3527306732.
External links
- Amino+Alcohols at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)