Great Yin 大殷 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 943–945 | |||||||||
 Map of Yin, 943 | |||||||||
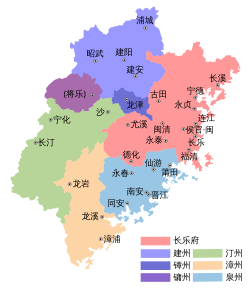 Map of Yin, early 945 | |||||||||
| Capital | Jian Prefecture (modern Jian'ou) | ||||||||
| Common languages | Middle Chinese Medieval Min Chinese | ||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||
| Emperor | |||||||||
• 943–945 | Wang Yanzheng | ||||||||
| Historical era | Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period | ||||||||
• Rebellion of Yin by Wang Yanzheng | 943 | ||||||||
• Ended by Southern Tang | 945 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of | China | ||||||||
The Yin (Chinese: 殷; pinyin: Yīn), officially the Great Yin (大殷), was a short-lived kingdom during China's Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period which lasted from 907 to 960 and bridged the time between the fall of the Tang dynasty and the foundation of the Song dynasty.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:252 9485831 726
-
Discovering China - The Song Dynasty
-
"Changsha Nü Yin"《长沙女引》from the Dunhuang pipa scores (Tang Dynasty) - version 2
-
General History of China EP52 | Five Dynasty and Ten Kingdoms | China Movie Channel ENGLISH | ENGSUB
Transcription
Rebellion from Min
The Min kingdom was founded in 909 after the Tang dynasty collapsed. However, after the founder of the kingdom, Wang Shenzhi, died in 925, the sons squabbled with one another. In 943, that led to an all out rebellion as one of Wang Shenzhi's sons, Wang Yanzheng, rebelled and carved out the Yin Kingdom out of the northwestern part of the Min kingdom.
Territorial extent
The Yin kingdom was rather small, occupying an area in present-day northern Fujian and southern Zhejiang. It was bounded by Wuyue to the north, Min to the south and east and the Southern Tang to the west.
End of Yin as separate entity
In 944, Wang Yanzheng's brother and rival as the Emperor of Min, Wang Yanxi, was assassinated. Wang Yanxi's general Zhu Wenjin claimed the Min throne. In 945, Zhu was assassinated, and his army pledged allegiance to Wang Yanzheng as the Emperor of Min and asked him to return to the Min capital Changle. Wang Yanzheng claimed the Min throne, ending Yin's existence as a separate state, but did not return to Changle; rather, he remained at his base of Jian Prefecture, which Southern Tang besieged later in the year, forcing his surrender.[1][2]
Ruler
| Temple Names ( Miao Hao 廟號) | Posthumous Names ( Shi Hao 諡號 ) | Personal Names | Period of Reigns | Era Names (Nian Hao 年號) and their according range of years |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Did not exist | Tian De Di (天德帝 Tiān Dédì) (as Emperor of Yin) | 王延政 Wáng Yánzhèng | 943–945 | Tiande (天德 Tiān Dé) 943–945 |
References
- ^ Zizhi Tongjian, vol. 284.
- ^ Zizhi Tongjian, vol. 285.
- Mote, F.W. (1999). Imperial China (900–1800). Harvard University Press. pp. 11, 16. ISBN 978-0-674-01212-7.
