| Greater hedgehog tenrec[1] | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Afrosoricida |
| Suborder: | Tenrecomorpha |
| Family: | Tenrecidae |
| Genus: | Setifer Froriep, 1806 |
| Species: | S. setosus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Setifer setosus (Schreber, 1778)
| |
| |
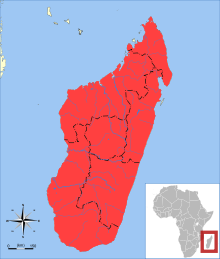
| Greater hedgehog tenrec range | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
The greater hedgehog tenrec (Setifer setosus), also known as the large Madagascar hedgehog or sokina,[3] is a species of mammal in the family Tenrecidae. It is endemic to Madagascar. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical forests, shrubland and grassland, savanna, rural gardens, and urban areas.[2]
It is the only species in the genus Setifer.[1] Despite the close resemblance, it is not closely related to hedgehogs. Similarly to hedgehogs, neoplasia is common within the species and plays a significant role in morbidity and mortality.[4]
Distribution and habitat
Greater hedgehog tenrecs are found throughout the island of Madagascar and are endemic to this island.[5]
The island of Madagascar ranges from sea level to 2,250 meters above sea level, and Setifer setosus is found throughout the island, with the exception of wetlands and marshes. Greater hedgehog tenrecs are seen in urban areas and even in areas with extensive human disturbance. The prime habitat for greater hedgehog tenrecs are the eastern forests and lower elevations because of their eating habits, but they are found in wet and dry areas.[5]
References
- ^ a b Bronner, G.N.; Jenkins, P.D. (2005). "Order Afrosoricida". In Wilson, D.E.; Reeder, D.M (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 77. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- ^ a b Stephenson, P.J.; Soarimalala, V.; Goodman, S. (2016). "Setifer setosus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T40594A97203842. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T40594A97203842.en. Retrieved 16 November 2021.
- ^ Imerina Malagasy common name used in Stratégie Nationale pour la Gestion Durable de la Biodiversité, publication of the Malagasy Ministry of the Environment Read the PDF
- ^ Khoii, Mina K.; Howerth, Elizabeth W.; Burns, Roy B.; Carmichael, K. Paige; Gyimesi, Zoltan S. (September 2008). "Spontaneous Neoplasia in Four Captive Greater Hedgehog Tenrecs (Setifer setosus)". Journal of Zoo and Wildlife Medicine. 39 (3): 392–397. doi:10.1638/2007-0063.1. ISSN 1042-7260. S2CID 22059010.
- ^ a b Owens, Rachel. "Setifer setosus (greater hedgehog tenrec)". Animal Diversity Web. Retrieved 2021-02-09.

