| Gemelli muscles | |
|---|---|
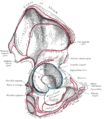
 The gemelli muscles and the internal obturator muscle | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Ischiopubic ramus and obturator membrane |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
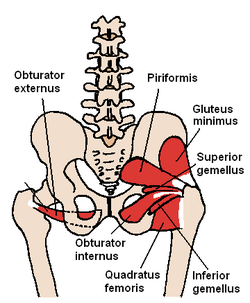
The gemelli muscles are the inferior gemellus muscle and the superior gemellus muscle, two small accessory fasciculi to the tendon of the internal obturator muscle. The gemelli muscles belong to the lateral rotator group of six muscles of the hip that rotate the femur in the hip joint.
Superior gemellus muscle

The gemelli muscles are two small muscular fasciculi, accessories to the tendon of the internal obturator muscle which is received into a groove between them. The superior gemellus muscle is the higher placed gemellus muscle that arises from the outer (gluteal) surface of the ischial spine, and blends with the upper part of the tendon of the internal obturator. It is smaller than the inferior gemellus. In some people, the fibres of the gemellus superior extend further than average, and are prolonged onto the medial surface of the greater trochanter of the femur.[1]
The superior and inferior gemelli are supplied by the inferior gluteal artery. Nerve supply to the superior gemellus is from the supply to the internal obturator – L5, S1, and S2.[2]
Inferior gemellus muscle
The inferior gemellus muscle arises from the upper part of the ischial tuberosity, immediately below the groove for the internal obturator tendon. It blends with the lower part of the tendon, and is inserted with it into the medial surface of the greater trochanter. It is rarely absent.
Like the internal obturator muscle, the gemellus superior and gemellus inferior help to steady the femoral head in the acetabulum. Both muscles also help to laterally rotate the extended thigh and abduct the flexed thigh at the hip by assisting the internal obturator.[1] The gemelli muscles act to compensate the reduced power of the internal obturator as it turns around the lesser sciatic notch.[1]
Blood supply is from the inferior gluteal artery. Nerve supply is from the supply to the quadratus femoris – L4 to S1.[2]
Etymology
Gemellus is the diminutive of "geminus"[clarification needed] meaning twin, doubled or duplicated. The superior and inferior gemellus muscles are paired and perform the same action.
Additional images
-
Superior gemellus muscle.
-
Right hip bone. External surface.
-
Right femur. Anterior surface.
References
- ^ a b c Palastanga, Nigel; Soames, Roger (November 2011). Physiotherapy Essentials : Anatomy and Human Movement : Structure and Function (6th ed.). London, GBR: Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 235–237. ISBN 9780702035531.
- ^ a b Miniato, Mohammed A.; Black, Asa C.; Varacallo, Matthew (2023), "Anatomy, Back, Lumbosacral Trunk", StatPearls, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, PMID 30969700, retrieved 2023-12-28
External links
- Anatomy photo:13:st-0402 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- PTCentral
- Univ. of Wash. Radiology