The Perpetual Peace or the Treaty of Eternal Peace (Greek: ἀπέραντος εἰρήνη[1]), signed in 532 between the East Roman (Byzantine) Empire and Sassanid Persia, was a peace treaty of indefinite duration, which concluded the Iberian War (527–531) between the two powers. It heralded a period of relatively cordial relations, but lasted only until 540, when hostilities resumed over the control of Lazica.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:607300 534568
-
INTRO (The State) Kant
-
Khosrau Anushirawan: Trolling Justinian - Extra History - #4
-
Memorial Retreat 2016
Transcription
History
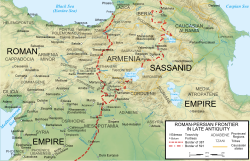
The Iberian War, which had been provoked by the uprising of the Iberians against the Persians in 524/5, had been largely indecisive: the Persians swiftly crushed the revolt, but were unable to make any gains in Byzantine territory except for two forts, Scanda and Sarapanis, in Lazica. The Byzantines had recovered from some early reversals to inflict two major defeats on the Persians in 530 at Dara and Satala. In their aftermath, they gained the two border forts of Bolum and Pharangium in Persarmenia, but were in turn defeated at Callinicum in 531. Throughout these conflicts, periods of truce and negotiations were interspersed with campaigns, but these had led to no concrete results.[2]
With the death of the Persian shahanshah Kavadh I (r. 488–531) in late 531, however, and the accession of his third son Khosrau I (r. 531–579), the situation changed: Khosrau's domestic position was insecure, while on the Byzantine side, Emperor Justinian I (r. 527–565) was perhaps already more focused on recovering the lost western half of the Roman Empire than in pursuing war against Persia.[3] The Byzantine envoys Rufinus, Hermogenes, Alexander and Thomas found Khosrau in a more conciliatory disposition than his father, and an agreement was soon reached. Justinian would pay 110 centenaria (11,000 pounds) of gold, ostensibly as a contribution to the defence of the Caucasus passes against the barbarians living beyond, and the base of the dux Mesopotamiae would be withdrawn from the fortress of Dara to the city of Constantina. The two rulers would recognize once again each other as equal and pledged mutual assistance.[3][4] Khosrau initially refused to hand back the two Lazic forts, while demanding the return of the two other forts the Byzantines had captured in Persian Armenia. Justinian at first agreed, but soon changed his mind, causing the agreement to be broken off. In summer 532, however, a new embassy by Hermogenes and Rufinus managed to persuade Khosrau for a full exchange of the occupied forts, as well as for allowing the exiled Iberian rebels to either remain in the Byzantine Empire or return unmolested to their homes.[5]
The next few years were marked by a remarkably cordial atmosphere and cooperation between the Middle East's two great powers. During that time, however, as Justinian focused his energy and resources in his wars of reconquest against the Vandals and in Italy against the Goths, the defenses of the East were neglected. This presented a golden opportunity for Khosrau, who, urged by Gothic envoys and anxious to fill his depleted state coffers with booty, began a new war in summer 540.[4][6]
References
- ^ Procopius. Persian War, 1.22.17.
- ^ Greatrex & Lieu 2002, pp. 82–96.
- ^ a b Greatrex & Lieu 2002, p. 96.
- ^ a b Maas 2005, p. 488.
- ^ Greatrex & Lieu 2002, pp. 96–97.
- ^ Greatrex & Lieu 2002, pp. 97–102.
Sources
- Greatrex, Geoffrey; Lieu, Samuel N. C. (2002). The Roman Eastern Frontier and the Persian Wars (Part II, 363–630 AD). New York, New York and London, United Kingdom: Routledge (Taylor & Francis). ISBN 0-415-14687-9.
- Maas, Michael, ed. (2005). The Cambridge Companion to the Age of Justinian. Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-81746-2.
Further reading
- Börm, Henning (2007). Prokop und die Perser: Untersuchungen zu den römisch-sasanidischen Kontakten in der ausgehenden Spätantike. Stuttgart, Germany: Franz Steiner Verlag. pp. 299–307 and 326–332. ISBN 978-3-515-09052-0.
